The Influence of Teacher Curriculum Leadership on the Implementation Effectiveness of Curriculum Ideological and Political Education
Abstract
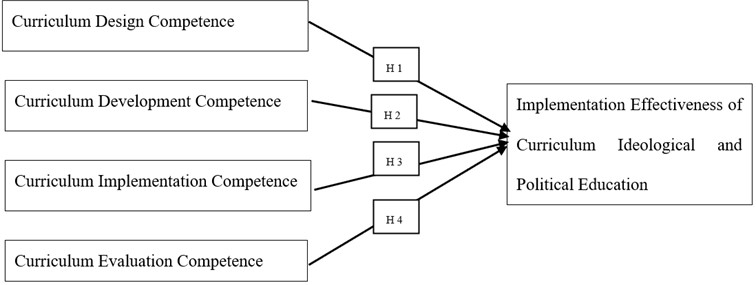
The study looks into how ideological and political education in college English courses is influenced by teachers’ curriculum leadership, respecting their curriculum design competence, curriculum development competence, curriculum implementation competence, and curriculum evaluation competence. Cronbach's Alpha in a pilot test (n=30) was adopted for the reliability test of the instruments and Index of Item-Objective Congruence (IOC) was investigated for the validity test. The study resorted to Multiple linear regression analysis to confirm the substantial link between variables in 630 (30 from teachers and 600 from students) valid replies from SUMC (Sichuan University of Media and Communications). Multiple linear regression analysis results showed that the ideological and political education in college English courses was strongly impacted by each of the four independent variables. This study examined four key factors in the context of private schools in Sichuan, China, and provided some guidance on how to improve curricular leadership among instructors in order to enhance curriculum ideological and political education in higher education.
References
Daehling, W. (1981). Curriculum research and development in action by Lawrence Stenhouse.Educational Communication and Technology Journal, 2, 130-131.
Gao, D. Y. (2017). The theoretical connotation and practical path of curriculum-based ideological and political education. Journal of Ideological & Theoretical Education, 12, 11–14.
Harris, A. (2003). Teacher leadership as distributed leadership: heresy, fantasy or possibility?. School Leadership and Management, 23(3), 313-324. https://doi.org/10.1080/1363243032000112801
Hu, J. H. (2021). Research on instructional design from the perspective of ideological and political education in foreign language courses. China Foreign Languages, 18(3), 53-59. https://doi.org/10.13564/j.cnki.issn.1672-9382.2021.03.007
Hu, Y., Shi, L. Y., & Li, M. (2019). Ideological and political education design and evaluation methods in medical microbiology courses. Medical Education Research and Practice, 37(3), 476–479.
Li, L., & Sun, Y. Y. (2019). A preliminary study on the implementation effectiveness of ideological and political education. Journal of Shaoxing University, 10, 16–20.
Ministry of Education. (2020). Guiding Outline for Ideological and Political Education in Higher Education Curriculum. http://www.moe.gov.cn
National Advisory Committee on College Foreign Language Teaching. (2020). College English teaching guidelines. Higher Education Press.
Passow, A. H. (1954). Organization and procedures for curriculum improvement. Review of Educational Research, 3, 221-236.https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543024003221
Richards, J. C. (2017). Curriculum development in language teaching (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009024556
Shulman, L. S. (1987). Knowledge and teaching: Foundations of the new reform. Harvard Educational Review, 57(1), 1-23. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.57.1.j463w79r56455411
Song, S. J. (2021). A review of literature on the effectiveness evaluation of ideological and political education in teaching. Science Information, 27, 91-92.
Stenhouse, L., Rudduck, J., & Hopkins, D. (1985). Research as a basis for teaching: readings from the work of Lawrence Stenhouse. Heinemann Educational Books.
Wang, C. (2022). Research on curriculum leadership of international Chinese language teachers in universities (Unpublished doctoral dissertation0. Northeast Normal University.
Wang, F., Zhang, B. W., & Zhang, Y. T. (2021). Investigation and countermeasures on the implementation effectiveness of ideological and political education in postgraduate cultivation. University Education, 4, 116–118.
Wan, J., & Ma, Y. T. (2017). Performance evaluation of ideological and political education in universities from students' perspectives. Theory Longitude and Latitude, SI, 294–300.
Wang, M., & Zhu, Y. X. (2020). Progress and prospects in teacher leadership research. Chinese Journal of Education Science, 7, 130–134.
Wen, Q. F. (2021). The connotation and implementation framework of ideological and political education in college English courses. China Foreign Languages, 18(2), 47–52.
Wu, Q. R., & Ke, X. (2021). Review and prospect: A research review on the evaluation of ideological and political education effectiveness in higher education. Journal of Higher Education, 25, 168–172.
Wang, S. F. (2020). Exploring the research framework of teachers’ curriculum leadership. Social Science Front, 11, 274–280.
Yang, Y. (2017). Teachers’ curriculum leadership: Sources, elements, and cultivation. Contemporary Teacher Education, 3, 67–72.
Zhou, L. M., Yuan, L. P., & Mei, M. Y. (2022). Constructing effective classroom environments and evaluation scales for ideological and political education in foreign language courses. China Foreign Languages, 7, 21–29.
Zhao, S. Y., Guo, L. X., & Chen, X. M. (2019). Evaluation criteria for the educational effectiveness of ideological and political education in "Mechanical Drawing and CAD" courses. Mechanical & Electrical Technology, 2, 103–105, 120.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








1.png)

















