Validation Syndrome: The Root of Deception and Developmental Predictors of Dark Triad Traits in Adolescents for Forensic and Developmental Psychology
Abstract
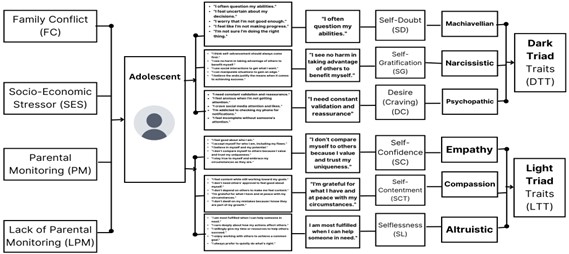
This study examines the early developmental predictors of Dark Triad traits, narcissism, machiavellianism, and psychopathy in adolescents using a mixed-methods approach grounded in the Validation Syndrome Diagnostic Triangle (VSDT) framework. The VSDT posits that self-doubt, desire, and self-gratification interact with environmental and familial influences to shape personality traits. Data from the Add Health Longitudinal Study (N = 15,000 adolescents, aged 12–18) were analyzed using Pearson correlations, multiple regression, and thematic analysis. Findings indicate that familial conflict and socioeconomic stress strongly predict Dark Triad tendencies, particularly self-doubt (r = .953, p < .05), self-gratification (r = .898, p < .05), and desire (r = .812, p < .05). Conversely, parental monitoring demonstrated a protective effect, negatively correlating with self-doubt (β = -0.008, p < .05) and self-gratification (β = 0.269, p < .05). Regression analysis identified familial conflict as the strongest predictor of maladaptive traits (β = 0.158, p < .001), accounting for 92.68% of the variance in self-doubt (R² = .927). Thematic analysis corroborated these findings, linking Dark Triad traits to validation-seeking behaviors in adverse familial environments. Adolescents with high Dark Triad tendencies engaged in cyberbullying and manipulative online behaviors, while supportive environments and parental monitoring fostered resilience. These findings validate the VSDT framework, emphasizing the role of familial and environmental factors in adolescent personality development. The findings have implications for forensic cyberpsychology, examining how online interactions shape developmental patterns and influence digital deception. The study provides actionable insights for early interventions to mitigate antisocial behavior. Future research should explore cross-cultural interventions to support healthier adolescent development.
References
[2] Milenkova, V., & Nakova, A. (2023). Personality development and behavior in adolescence: Characteristics and dimensions. Societies, 13(6), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/SOC13060148
[3] Yinxin, Y. (2021). Adolescent personality development and its influencing factors. Journal of Sociology and Ethnology, 3(7), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.23977/JSOCE.2021.030701
[4] Basto-Pereira, M., Farrington, D. P., & Maciel, L. (2024). Unraveling the Sequences of Risk Factors Underlying the Development of Criminal Behavior. Journal of Developmental and Life-Course Criminology, 10(2), 242–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40865-024-00254-5/TABLES/4
[5] Loggen, J., Moneva, A., & Leukfeldt, R. (2024). A systematic narrative review of pathways into, desistance from, and risk factors of financial-economic cyber-enabled crime. Computer Law & Security Review, 52, 105858. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLSR.2023.105858
[6] Miller, A., & Johnston, C. A. (2024). Family structure and material hardship: Child and adolescent pathways to health and well-being. Infant and Child Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/ICD.2510
[7] Wissing, B. G., & Reinhard, M. A. (2019). The dark triad and deception perceptions. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(AUG). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01811
[8] Thomsen, L., & Homel, R. (2024). Cumulative sociodemographic risk as a predictor of adolescent antisocial behaviour. Child Indicators Research, 17(5), 2123–2148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-024-10157-y
[9] Viding, E., McCrory, E., Baskin-Sommers, A., De Brito, S., & Frick, P. (2024). An ‘embedded brain’ approach to understanding antisocial behaviour. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 28(2), 159–171. Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2023.08.013
[10] Carroll, S. L. (2024). The Origins of Antisocial Behavior: Influences of Genes, Development, and Context (Publication No. 3123917696) [Doctoral dissertation, Michigan State University]. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. Available at: https://login.captechu.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/origins-antisocial-behavior-influences-genes/docview/3123917696/se-2
[11] Huang, Y., Gan, X., Jin, X., Rao, S., Guo, B., He, Z., & Wei, Z. (2023). The relationship between the Dark Triad and bullying among Chinese adolescents: The role of social exclusion and sense of control. Frontiers in Psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1173860
[12] Chow, R. T. S., Yu, R., Geddes, J. R., & Fazel, S. (2024). Personality disorders, violence and antisocial behavior: Updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2024.226
[13] Abhishek, R., & Balamurugan, J. (2024). Impact of social factors responsible for Juvenile delinquency – A literature review. Journal of Education and Health Promotion, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.4103/JEHP.JEHP_786_23
[14] Martineau, M., Spiridon, E., & Aiken, M. (2023). A comprehensive framework for cyber behavioral analysis based on a systematic review of cyber profiling literature. Forensic Sciences, 3(3), 452–477. https://doi.org/10.3390/FORENSICSCI3030032
[15] McGovern, R., Balogun-Katung, A., Artis, B., Bareham, B., Spencer, L., Alderson, H., Brown, E., Brown, J., Lingam, R., McArdle, P., Newham, J. J., Wojciechowska, A., Rankin, J., Redgate, S., Thomason, P., & Kaner, E. (2024). The effectiveness of preventative interventions to reduce mental health problems in at-risk children and young people: A systematic review of reviews. Journal of Prevention, 45(4), 651–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-024-00785-z
[16] Ogonowska, A. (2023). Cyberpsychology and media studies: Contemporary research directions and sources of mutual inspiration. Annals of Psychology, 26(4), 315–330. https://doi.org/10.18290/RPSYCH2023.0017
[17] Rich, M. S., & Aiken, M. P. (2024). An interdisciplinary approach to enhancing cyber threat prediction utilizing forensic cyberpsychology and digital forensics. 1 Forensic Sciences, 4(1), 110–151. https://doi.org/10.3390/forensicsci4010008
[18] Liang, T., Wang, X., Ng, S., Xu, X., & Ning, Z. (2024a). The dark side of mental toughness: A meta-analysis of the relationship between the dark triad traits and mental toughness. Frontiers in Psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1403530
[19] Smaragdi, A., Schwarz, L. J., Austevik, T. J., Walsh, M., Webster, C., & Augimeri, L. (2024). Inter-rater reliability of the Early Assessment Risk List Version 3 (EARL-V3) for children displaying antisocial behavior. Children and Youth Services Review, 164, 107824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2024.107824
[20] Cheng, C. H., Tein, J. Y., Shaw, D. S., Wilson, M. N., & Lemery-Chalfant, K. (2025). Predictors of stability/change in observed parenting patterns across early childhood: A latent transition approach. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 70, 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2024.09.002
[21] Cheng, W. Y., Cheung, R. Y. M., & Chung, K. K. H. (2024). The role of family conflict and cohesion in adolescents’ social responsibility: Emotion regulation ability as a mediator. PLOS ONE, 19(9), e0311265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0311265
[22] Barnhart, S., Garcia, A. R., & Karcher, N. R. (2022). Adolescent Mental Health and Family Economic Hardships: The Roles of Adverse Childhood Experiences and Family Conflict. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 51(12), 2294–2311. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10964-022-01671-9
[23] Martínez-Casanova, E., Molero-Jurado, M. del M., & Pérez-Fuentes, M. del C. (2024). Self-esteem and risk behaviours in adolescents: A systematic review. Behavioral Sciences, 14(6), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/BS14060432
[24] Petrica, E., & Panisoara, G. (2024). The influence of Dark Triad-specific personality traits (Machiavellianism, narcissism, psychopathy) on parenting styles and parental competence in raising and educating children. Global Journal of Social Sciences Studies, 10(2), 68–75. https://doi.org/10.55284/gjss.v10i2.1182
[25] Gubbels, J., Assink, M., & van der Put, C. E. (2024). Protective factors for antisocial behavior in youth: What is the meta-analytic evidence? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 53(2), 233–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01878-4
[26] Huynh, H. P., Thomas, J., Castellanos, I., Weatherford, D. R., & Lilley, M. K. (2024). Social comparison, belongingness, self-doubt, and stress: The case of Hispanic students at Hispanic majority institutions. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 46(2), 99–121. https://doi.org/10.1177/07399863241292243
[27] García-Sastre, M. M., González-Alegre, P., Luengo-González, R., Cuesta-Lozano, D., Rodríguez-Rojo, I. C., Lluch-Canut, T., & Peñacoba-Puente, C. (2024). Promoting mental health in adolescents: “Teens Mental+”, a nursing intervention program based in the positive mental health model. Psychology International, 6(3), 710–721. https://doi.org/10.3390/PSYCHOLINT6030044
[28] Hastings, P. D., Miller, J. G., Weissman, D. G., Hodge, R. T., Robins, R. W., Carlo, G., & Guyer, A. E. (2024). Parasympathetic regulation and support from family and friends predict prosocial development in U.S. Mexican-origin adolescents. Developmental Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/DEV0001780
[29] Kaufman, S. B., Yaden, D. B., Hyde, E., & Tsukayama, E. (2019a). The light vs. dark triad of personality: Contrasting two very different profiles of human nature. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(MAR). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00467
[30] Lee, I., Chang, Y., Lei, Y., & Yoo, T. (2024b). Adolescent health and dark personalities: The role of socioeconomic status, sports, and cyber experiences. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(8), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH21080987
[31] Ashraf, A., Khan, M. L., & Atta, N. (2024). Permissive Parenting, Self Regulation and Risk-Taking Behavior among Adolescents. Global Social Sciences Review, IX(I), 89–101. [https://doi.org/10.31703/GSSR.2024(IX-I).09](https://doi.org/10.31703/GSSR.
[32] Yang, R. (2024). The influence of the parenting style on children’s social ability and developmental ability. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 33(1), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7048/33/20231508
[33] Gómez-Leal, R., Fernández-Berrocal, P., Gutiérrez-Cobo, M. J., Cabello, R., & Megías-Robles, A. (2024a). The dark tetrad: Analysis of profiles and relationship with the Big Five personality factors. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-55074-w
[34] Szabó, Z. P., Orosz, N. Z., Gulyás, R., & Láng, A. (2024a). The associations of peer-rated popularity and likeability with Dark Triad personality traits in adolescent groups. Europe’s Journal of Psychology, 20(3), 165–177. https://doi.org/10.5964/EJOP.11667
[35] Song, H., Chan, J. S., & Ryan, C. (2024). Differences and similarities in the use of nine emotion regulation strategies in Western and East-Asian cultures: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220221241285006
[36] Jones, L. (2024). Unveiling human factors: Aligning facets of cybersecurity leadership, insider threats, and arsonist attributes to reduce cyber risk. SocioEconomic Challenges, 8(2), 44–63. https://doi.org/10.61093/sec.8(2).44-63.2024
[37] Putri, A. A. T., Parwatha, N. W., Sutrisna, I. P. B., & Wiguna, I. G. R. P. (2024). Parenting models, spirituality and personality disorders in adolescence. International Journal of Health & Medical Sciences, 7(2), 40–52. https://doi.org/10.21744/ijhms.v7n2.2279
[38] Mutie Wambua, F., & S. K., F. (2024). Influence of neglectful parenting approaches on self-esteem of teenagers aged 13–19 years in selected day secondary schools in Lari Sub County in Kiambu County, Kenya. International Journal of Psychology, 9(3), 15–30. https://doi.org/10.47604/IJP.2648
[39] Brazil, K. J., Farrell, A. H., Boer, A., & Volk, A. A. (2024). Adolescent psychopathic traits and adverse environments: Associations with socially adaptive outcomes. Development and Psychopathology, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579424000051
[40] Ceroni, D. B., & Yalch, M. M. (2024). Influence of childhood maltreatment on Machiavellianism. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 33(9), 1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2024.2358870
[41] Pérez-Torres, V. (2024). Social media: A digital social mirror for identity development during adolescence. Current Psychology, 43(26), 22170–22180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05980-z
[42] Charmaraman, L., Hojman, H., Auqui, J. Q., & Bilyalova, Z. (2024). Understanding adolescent self-esteem and self-image through social media behaviors. Pediatric Clinics of North America, 0(0). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2024.07.034
[43] Tan, C. N.-L., & Fauzi, M. A. (2024). Unravelling late adolescents’ addiction to social media: A unified theory perspective. Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication. https://doi.org/10.1108/GKMC-02-2024-0099
[44] di Giacomo, E., Andreini, E., Lorusso, O., & Clerici, M. (2023). The dark side of empathy in narcissistic personality disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1074558
[45] Xu, F. (2024). The relationship between family function and aggression in peer relationships among adolescents. Journal of Education, Humanities and Social Sciences IMPES, 2023. https://doi.org/10.54097/2ev1xt38
[46] Toro-Alvarez, M. M. (2024). Digital violence in schools: A unified theory and structural equation model to counteract cyberbullying. Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research. https://doi.org/10.1108/JACPR-03-2024-0886
[47] Myznikov, A., Korotkov, A., Zheltyakova, M., Kiselev, V., Masharipov, R., Bursov, K., Yagmurov, O., Votinov, M., Cherednichenko, D., Didur, M., & Kireev, M. (2024a). Dark triad personality traits are associated with decreased grey matter volumes in ‘social brain’ structures. Frontiers in Psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1326946
[48] Moreira, D., Azeredo, A., Ramião, E., Figueiredo, P., Barroso, R., & Barbosa, F. (2024). Systematic exploration of antisocial behavior. European Psychologist, 29(2), 108–122. https://doi.org/10.1027/1016-9040/A000527
[49] Leota, J., Faulkner, P., Mazidi, S., Simpson, D., & Nash, K. (2024). Neural rhythms of narcissism: Facets of narcissism are associated with different neural sources in resting-state EEG. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 60(5), 4907–4921. https://doi.org/10.1111/EJN.16479
[50] Add Health. (2019). The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (Add Health). https://addhealth.cpc.unc.edu/
[51] DSDR. (2022). National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (Add Health) Data Guide 1994-2018. https://www.icpsr.umich.edu/web/pages/DSDR/add-health-data-guide.html
[52] Harris, K. M. (2020). Guidelines for analyzing Add Health data. https://doi.org/10.17615/C6BW8W
[53] Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2019). Reflecting on reflexive thematic analysis. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health, 11(4), 589–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/2159676X.2019.1628806
[54] Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2024). Supporting best practice in reflexive thematic analysis reporting in Palliative Medicine: A review of published research and introduction to the Reflexive Thematic Analysis Reporting Guidelines (RTARG). Palliative Medicine, 38(6), 608–616. https://doi.org/10.1177/02692163241234800
[55] Naeem, M., Ozuem, W., Howell, K., & Ranfagni, S. (2023). A step-by-step process of thematic analysis to develop a conceptual model in qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 22. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069231205789
[56] Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2013). Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. 3rd edn. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203774441
[57] Busetto, L., Wick, W., & Gumbinger, C. (2020). How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurological Research and Practice, 2(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/S42466-020-00059-Z/TABLES/1
[58] de Moor, E. L., Nelemans, S. A., Becht, A. I., Meeus, W., & Branje, S. (2023). Personality development across adolescence and young adulthood: The role of life transitions and self-concept clarity. European Journal of Personality, 37(5), 587–604. Available at: https://osf.io/nhs5t
[59] Miller, P., Blatt, L., Hunter-Rue, D., Barry, K. R., Jamal-Orozco, N., Hanson, J. L., & Votruba-Drzal, E. (2024a). Economic hardship and adolescent behavioral outcomes: Within- and between-family associations. Development and Psychopathology. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579423001451
[60] Hillman, J. G., Fowlie, D. I., & MacDonald, T. K. (2023). Social verification theory: A new way to conceptualize validation, dissonance, and belonging. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 27(3), 309–331. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/10888683221138384
[61] de Moor, E. L., Nelemans, S. A., Becht, A. I., Meeus, W., & Branje, S. (2023). Personality development across adolescence and young adulthood: The role of life transitions and self-concept clarity. European Journal of Personality, 37(5), 587–604. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/08902070221119782
[62] Grotevant, H. D., Lo, A. Y. H., Fiorenzo, L., & Dunbar, N. D. (2017). Adoptive identity and adjustment from adolescence to emerging adulthood: A person-centered approach. Developmental Psychology, 53(11), 2195–22
[63] Ferencz, T., Láng, A., Kocsor, F., Kozma, L., Babós, A., & Gyuris, P. (2023). Sibling relationship quality and parental rearing style influence the development of Dark Triad traits. Current Psychology, 42(28), 24764–24781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03506-z
[64] Abhishek, R., & Balamurugan, J. (2024). Impact of social factors responsible for juvenile delinquency – A literature review. Journal of Education and Health Promotion, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.4103/JEHP.JEHP_786_23
[65] Arbel, R. (2024). Daily profiles of parents’ supportive extrinsic emotion regulation of adolescents’ negative emotion. Emotion. https://doi.org/10.1037/EMO0001377
[66] Wang, M. (2024). Social anxiety in adolescents: An analysis of the psychological influence mechanism of social media use. International Journal of Education and Humanities, 16(3), 55–58. https://doi.org/10.54097/ry4jbb84
[67] Xing, H., Zhang, Y., Yao, M., Zhu, W., & Liu, H. (2024). How perceived parenting qualities link to the reciprocal relationship between adolescents’ self-concept and life satisfaction. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships. https://doi.org/10.1177/02654075241268780
[68] Stern, J. A., Bailey, N. A., Costello, M. A., Hellwig, A. F., Mitchell, J., & Allen, J. P. (2024). Empathy across three generations: From maternal and peer support in adolescence to adult parenting and child outcomes. Child Development. https://doi.org/10.1111/CDEV.14109
[69] Jiang, X., Liu, C., Xiao, X., & Zhan, Y. (2024). Role of narcissism and empathy in the relationship between parental attachment and moral response patterns. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 21(3), 365–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/17405629.2024.2325173
[70] Li, F., Gou, C., Tang, X., Qiu, Y., Deng, M., & Ji, X. (2024). Parental warmth, friendship quality, empathy and bystander defending behavior in cyberbullying among adolescents in China. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2024.2374712
[71] Çelik, O. (2024). Academic motivation in adolescents: The role of parental autonomy support, psychological needs satisfaction and self-control. Frontiers in Psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYG.2024.1384695
[72] Hong, Y. K., & Choi, H.-J. (2024). Multiple mediating effects of autonomy, competence and relatedness on the relation between parents’ autonomy support and adolescents’ career maturity. The Korea Parents Education Association, 21(1), 5–28. https://doi.org/10.61400/JPE.2024.21.1.05
[73] Kozyreva, V. V., & Pham, V. A. T. (2024). Correlation between emotional acceptance of parents and independence level of adolescents. Vestnik Universiteta, 5, 246–256. https://doi.org/10.26425/1816-4277-2024-5-246-256
[74] Edler, K., & Valentino, K. (2024). Parental self-regulation and engagement in emotion socialization: A systematic review. Psychological Bulletin, 150(2), 154–191. https://doi.org/10.1037/BUL0000423
[75] Lin, J., & Li, Y. (2024). A study of the effects of parental psychological control on adolescents’ self-control. Journal of Psychology and Behavior Studies, 4(1), 88–93. https://doi.org/10.32996/JPBS.2024.1.10
[76] Nisskaya, A. K., & Tsyganova, E. M. (2024). Parental practices of controlling and supporting the autonomy of elementary school children and early adolescents in Russia: A qualitative study. Psychology in Russia: State of the Art, 17(2), 3–22. https://doi.org/10.11621/PIR.2024.0201
[77] Islami, J. P., Fani, I., Nur, S., Latifa, R., & Napitupulu, L. (2024). Gratitude as a determinant of psychological well-being in adolescents: An Islamic psychology perspective. Psikis: Jurnal Psikologi Islami, 10(1), 167–174. https://doi.org/10.19109/PSIKIS.V10I1.21706
[78] Wong, Y. J., Pandelios, A. L., Carlock, K., & Thielmeyer, A. M. B. (2024). Stronger together: Perspectives on gratitude social processes in group interventions for adolescents. Frontiers in Psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPSYG.2024.1476511
[79] Lombardi, A. R., Rifenbark, G. G., Shogren, K. A., Taconet, A., & Hicks, T. A. (2024). Exploring the relationship between self-determination and economic hardship constructs among adolescents with and without disabilities. Remedial and Special Education. https://doi.org/10.1177/07419325241247343
[80] Peng, Y., Xia, M., & Chi, X. (2024). Age-varying associations of parent-adolescent relationship and school connectedness with adolescent self-compassion: Differences by gender. Journal of Adolescence. https://doi.org/10.1002/JAD.12378
[81] Krok, D., & Tkaczyk, J. (2024). The Light vs. Dark Triad and compassion for others: The mediating role of inner harmony among teachers. Archives of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, 26(3), 17–26. https://doi.org/10.12740/APP/183678
[82] Apriyeni, E., Patricia, H., & Rahayuningrum, D. C. (2024). Adolescents conflict resolution patterns: A descriptive analysis. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Approach Research and Science, 2(2), 813–821. https://doi.org/10.59653/IJMARS.V2I02.748
[83] Sitota, G., & Tefera, B. (2024). Family cohesion and disruptive behavior among school adolescents: The mediating role of self-regulation. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (IJERE), 13(1), 9–17. https://doi.org/10.11591/IJERE.V13I1.24969
[84] Lalita, R. (2024). Social competence and altruistic behaviour among adolescents: A review study. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.36948/IJFMR.2024.V06I01.12771
[85] Adinata, S. P., & Kesumaningsari, N. P. A. (2024). Adolescents cyberbullying: Examining the role of social media use intensity and Dark Triad personality. Journal of Educational, Health and Community Psychology, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.12928/jehcp.v13i4.28751
[86] Burton, S. L., Burrell, D. N., Nobles, C., & Jones, L. A. (2023). Exploring the Nexus of Cybersecurity Leadership, Human Factors, Emotional Intelligence, Innovative Work Behavior, and Critical Leadership Traits. Scientific Bulletin, 28(2), 162–175. https://doi.org/10.2478/BSAFT-2023-0016
[87] Davidson, J., Aiken, M., Phillips, K., & Farr, R. (2022). European youth cybercrime, online harm and online risk-taking: 2022 research report. CC-DRIVER 2021 European Youth Survey. Available at: https://repository.uel.ac.uk/item/8v59y
[88] Jones, L. A. (2021). A content analysis review of literature to create a usable framework for reputation risk management. In Advances in Cybersecurity Leadership: The Human Element, 91–133. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-3811-1.CH006
[89] Burrell, D. N., Nobles, C., Cusak, A., Jones, L. A., Wright, J. B., Mingo, H. C., Ferreras-Perez, J., Khanta, K., Shen, P., & Richardson, K. (2023). Cybersecurity and cyberbiosecurity insider threat risk management. In Handbook of Research on Cybersecurity Risk in Contemporary Business Systems, 121–136. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-7207-1.CH006
[90] Lim, J., & Huh, Z. (2024). Relationship between parental monitoring and cyberbullying perpetration among male and female adolescents: Dual sequential mediating effects of self-control and peer conformity of antisocial behaviors. Korea University Institute of Educational Research, 91, 139–165. https://doi.org/10.24299/kier.2024.372.139
[91] Castagna, P. J., & Hart, W. (2024). Light triad traits moderate the relationship between the dark tetrad and immoral character. Personality and Individual Differences, 222, 112593. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PAID.2024.112593

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








1.png)

















