Analysis of the Factors Influencing the Changes in Beach Landforms of Weizhou Island and Environmental Protection
Abstract
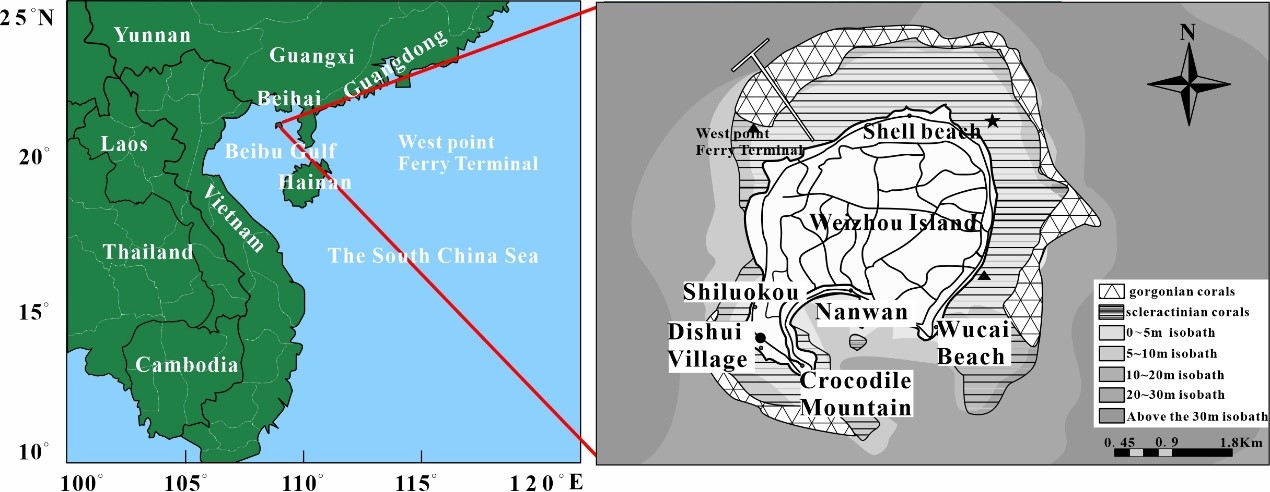
The beach is one of the main tourist resources of Weizhou Island. The quality of the beach landforms and coastal environment greatly influences the comfort and overall experience of tourists. This is primarily affected by both human and natural factors. Based on multiple field surveys conducted on Weizhou Island and previous research materials, this paper focuses on studying the changes in the Shiluokou-Dishuicun beach landforms of Weizhou Island and their impact on the ecological environment. The following four conclusions are drawn: 1) The degradation of coral reefs leads to coastal retreat; 2) Storm surges result in the destruction of coastal vegetation; 3) Headlands cause a large accumulation of coastal sediments; 4) Circulation is the main limiting factor for beach migration and expansion. Finally, based on the research conclusions, along with a superficial investigation and review of related materials on the coastal engineering at Yalong Bay, Hainan, specific suggestions for the protection of Weizhou Island's beach ecological environment are proposed.
References
Beihai Municipal People's Congress Standing Committee. (2018). Regulations on ecological environment protection of Weizhou Island, Beihai City.
Bitterwolf, S. A., Reguero, B. G., Storlazzi, C. D., & Beck, M. W. (2024). Shifting sands: The influence of coral reefs on shoreline erosion from short-term storm protection to long-term disequilibrium. Nature-Based Solutions, 6, 100174.
Cen, B. X. (2003). Basic ideas for the ecological tourism development of Weizhou Island, Beihai. Tourism Tribune(02), 69–72.
Chen, B. Z. (2021, December 23). Serious coastal erosion due to excessive development of the world's first bay "Yalong Bay," Sanya to invest 150 million RMB in ecological restoration. China Housing News.
Chen, H. (1999). Coral reef restoration on Weizhou Island: A mixed blessing. Coastal Environment(06), 29.
Chen, Y. Q., Zhong, X. M., Ju, Y. X., & Wei, L. M. (2024). Ecological environment status and protection suggestions for Weizhou Island. Ecological Environment and Protection, 7(11), 158–162.
East, H. K., Johnson, J. A., Perry, C. T., et al. (2023). Seagrass meadows are important sources of reef island-building sediment. Communications Earth & Environment, 4, 33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-023-00675-y
Gao, J. S., Wu, G. D., & Ya, H. Z. (2017). Review of the circulation in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 138, 106–119.
Harney, J. N., & Fletcher, C. H. (2003). A budget of carbonate framework and sediment production, Kailua Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 73, 856–868. https://doi.org/10.1306/051503730856
He, J. K., & Huang, Z. P. (2019). Study on the distribution of corals on Weizhou Island, Guangxi. Marine Development and Management, 36(01), 57–62.
Huang, H., Ma, B. R., Lian, J. S., Yang, J. H., Dong, Z. J., Fu, Q., & Liang, W. (2009). Current status of coral reefs in the waters of Weizhou Island, Guangxi, and its protection strategies. Tropical Geography, 29(04), 307–318.
Kench, P. S. (1998). Physical controls on development of lagoon sand deposits and lagoon infilling in an Indian Ocean atoll. Journal of Coastal Research, 14, 1014–1024.
Kuang, X. Y., Su, Z., & Tu, F. X. (2007). Climate zoning of Guangxi. Guangxi Science(03), 278–283.
Li, B. Y., & Zhong, H. M. (2013). Formation mechanism and control measures of steep cliff dangerous rocks in the Huguangyan Formation—A case study of the sea cliff in Nanwan Street, Weizhou Island. Technology and Market, 20(02), 49–50.
Li, M. J., Wu, S. H., Liu, Q. X., et al. (2015). Analysis of the impact of storm surges and tides on the erosion of the southwestern beach of Weizhou Island, Guangxi. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(9), 126–137.
Li, X., & Zhong, H. M. (2013). The formation mechanism and control measures of coastal erosion-prone rocks on the volcanic coast of Weizhou Island. Science and Technology Wind(05), 110–112.
Liang, W., Li, G. Z., Fan, H. Q., Wang, X., Nong, H. Q., Huang, H., Li, X. B., & Lan, G. B. (2010). Species composition and distribution characteristics of reef-building corals on Weizhou Island, Guangxi. Guangxi Science, 17(01), 93–96.
Liang, X., & Peng, Z. Q. (2018). Study and evaluation of water quality changes in the coral reef waters of Weizhou Island, Guangxi. Marine Development and Management, 35(01), 114–119.
Perry, C. T., Kench, P. S., Smithers, S. G., Riegl, B., Yamano, H., & O’Leary, M. J. (2011). Implications of reef ecosystem change for the stability and maintenance of coral reef islands. Global Change Biology, 17, 3679–3696. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.
Putnam, H. M., Barott, K. L., Ainsworth, T. D., & Gates, R. D. (2017). The vulnerability and resilience of reef-building corals. Current Biology, 27, R528–R540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.04.047
Roth, M. S. (2014). The engine of the reef: Photobiology of the coral-algal symbiosis. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 422. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00422
Tan, Q. Z., Wang, X., & Wu, L. C. (2021). Current status and trend of water quality in the sea area of Weizhou Island. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 48(20), 155-157.
Wang, G. Z., Quan, S. Q., & Lü, B. Q. (1991). Evolution of the modern sedimentary environment and sedimentary processes in the Weizhou Island region, South China Sea. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, (01), 69-82.
Wang, X., & Li, G. Z. (2009). Current status and future outlook of coral reef research on Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 25(01), 72-80.
Wu, L. P., & Zheng, X. H. (2024, June 10). Advancing coral reef resource protection and ecological restoration on Weizhou Island. Guangxi Daily, (8).
Xia, H. Y., & Gu, W. C. (2000). Statistical analysis of seawater temperature observations by marine stations along the Guangxi coastline. Marine Bulletin, (04), 15-21.
Yang, H., Wang, S. P., Yu, K. F., et al. (2017). Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in seawater in coral growth areas in the northern South China Sea. Journal of Ecological Environment, 26(02), 253-260.
Yao, Z. H., Gao, W., Gao, S., et al. (2013). Coastal erosion characteristics of Weizhou Island, Beihai, Guangxi. Coastal Engineering, 32(04), 31-40.
Ye, W. Q., Li, G. Z., Pang, Y. J., & Li, N. F. (1988). Coral reef coast and Quaternary sediment characteristics of Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf. Marine Science, (06), 13-17.
Yu, K. F., Jiang, M. X., Cheng, Z. Q., & Chen, T. G. (2004). Sea surface temperature changes over the past 42 years on Weizhou Island and their impact on coral reefs. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, (03), 506-510.
Yu, K. F., Jiang, M. X., Cheng, Z. Q., & Chen, T. G. (2004). Sea surface temperature changes over the past 42 years on Weizhou Island and their impact on coral reefs. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, (03), 506-510.
Zhao, L. (2018). Investigation and dynamic analysis of the erosion and sedimentation on the northeastern coast of Weizhou Island. Southern Land and Resources, (01), 37-40+44.
Zhong, H. M. (2013). The formation mechanism and control measures of coastal erosion-prone rocks on the volcanic coast of Weizhou Island. Science and Technology Wind, (05), 110-112.
Zhong, H. M., & Li, G. Z. (2013). Formation mechanism and control measures of steep cliff dangerous rocks in the Huguangyan Formation—A case study of the sea cliff in Nanwan Street, Weizhou Island. Technology and Market, 20(02), 49-50.
Zhou, H. L., & Li, G. Z. (2014). Health assessment of coral reefs on Weizhou Island. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 30(04), 238-247.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
























