Exploration and Practice of Ideological and Political Education in Additive Manufacturing Courses under the Concept of Green Intelligent Manufacturing
Abstract
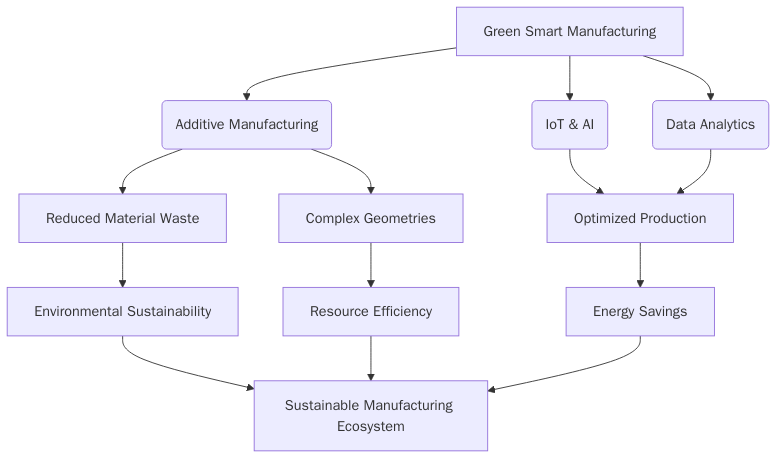
This paper explores the integration of ideological and political education into additive manufacturing courses within the framework of green smart manufacturing. Green smart manufacturing, which combines environmental sustainability with advanced intelligent technologies, emphasizes the harmonious coexistence of industrial activities and ecological preservation. Additive manufacturing, a key technology in this paradigm, significantly reduces material waste and enhances resource efficiency. However, current educational approaches often prioritize technical skills, neglecting ethical and sustainability dimensions. This study highlights the necessity of incorporating ideological and political education to cultivate a workforce aligned with sustainability and environmental responsibility. The paper outlines a systematic design for integrating these elements into the curriculum, teaching methods, and assessment strategies, ensuring students are equipped with both technical proficiency and ethical consciousness. Practical implementation and outcomes demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of this approach, fostering a generation of engineers committed to sustainable industrial practices. Challenges and recommendations for improvement are also discussed, paving the way for a more sustainable and ethically conscious industrial future.
References
Dong, F., et al. (2024). Dynamic job shop scheduling performance evaluation based on green intelligent manufacturing and thermal efficiency improvement. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsep.2024.102785
Du, Y. (2024). Exploration and practice of course ideological and political education in clinical skills training courses. International Journal of Global Economics and Management. https://doi.org/10.62051/ijgem.v2n3.36
Fu, B. (2024). Exploration of course ideological and political reform in cultural and art courses empowered by the metaverse. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal. https://doi.org/10.14738/assrj.114.16882
Hofmann, U., et al. (2023). Enhancing design for additive manufacturing education through a performance-based design challenge. Procedia CIRP. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2023.02.163
Li, J., et al. (2024). Exploration of the three-in-one professional course ideological and political teaching model of virtue, knowledge, and creativity: Taking the statistics major course probability theory as an example. World Education Forum. https://doi.org/10.18686/wef.v2i4.4584
Liao, C. (2023). Course ideological and political exploration and practice under professional ideological and political leadership. International Journal of Science and Engineering Applications. https://doi.org/10.7753/ijsea1205.1005
Pikkarainen, A., et al. (2020). Introducing novel learning outcomes and process selection model for additive manufacturing education in engineering. European Journal of Education Studies, 8. https://doi.org/10.46827/ejes.v8i1.3511
Prabhu, R., et al. (2020). Exploring the effects of additive manufacturing education on students’ engineering design process and its outcomes. Journal of Mechanical Design. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4044324
Prabhu, R., et al. (2020). Teaching design freedom: Understanding the effects of variations in design for additive manufacturing education on students’ creativity. Journal of Mechanical Design. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4046065
Su, Y., et al. (2024). Evaluating green technology innovation capability in intelligent manufacturing enterprises: A Z-number-based model. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 71, 5391–5409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2024.3350357
Tieng, H., et al. (2023). I4.2-GiM: A novel green intelligent manufacturing framework for net zero. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2023.3340149
Wei, X., et al. (2024). Towards green development: The role of intelligent manufacturing in promoting corporate environmental performance. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2024.107375
Yin, S., & Zhang, N. (2022). Enhancing engineering ethics education (EEE) for green intelligent manufacturing: Implementation performance evaluation of core mechanism of green intelligence EEE. Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.926133
Zhu, J. (2024). Exploration of course ideological and political education in higher vocational colleges railway passenger transport service major: Taking railway passenger transport service management as an example. World Education Forum. https://doi.org/10.18686/wef.v2i3.4286

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
























