Frontiers in Skin Rejuvenation: Recent Advances in Anti-Aging Skincare Technologies Based on Proteins, Peptides, and Peptide Derivatives
Abstract
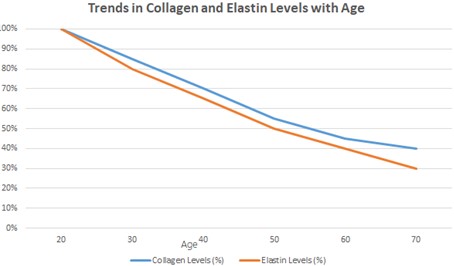
Skin aging, characterized by collagen and elastin degradation, reduced cellular turnover, and oxidative stress, leads to wrinkles, sagging, and uneven skin tone. The global anti-aging skincare market is projected to reach $421.4 billion by 2030, driven by the demand for innovative solutions. Proteins, peptides, and peptide derivatives have emerged as key ingredients in modern anti-aging skincare due to their ability to stimulate collagen synthesis, enhance hydration, and repair damaged skin. Peptide derivatives like acetyl hexapeptide-8 (Argireline) and palmitoyl pentapeptide-4 (Matrixyl) have been clinically proven to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity. Advanced technologies, such as nanotechnology and AI-driven formulations, enhance peptide stability and efficacy. The integration of peptides with stem cells and microbiome modulation offers comprehensive anti-aging solutions, while personalized skincare based on genetic profiling enables tailored treatments.The future of anti-aging skincare lies in sustainable and ethical practices, including plant-based peptides and eco-friendly packaging. These advancements promise to revolutionize the industry, delivering effective, personalized, and environmentally responsible solutions for skin rejuvenation.
References
[2] Kim, J. K., Lee, J. H., Yang, M. S., Seo, D. B., & Lee, S. J. (2009). Beneficial effect of collagen peptide supplement on anti-aging against photodamage. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology, 41(4), 441–445. https://doi.org/10.9721/KJFST.2012.44.4.441
[3] Lu, S., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., Ni, J., Zhao, T., & Xiao, G. (2024). Anti-skin aging effects and bioavailability of collagen tripeptide and elastin peptide formulations in young and middle-aged women. Journal of Dermatologic Science and Cosmetic Technology, 6(2), 100019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdsct.2024.100019
[4] Veiga, E., Ferreira, L., Correia, M., Pires, P. C., Hameed, H., Araújo, A. R. T. S., & Paiva-Santos, A. C. (2023). Anti-aging peptides for advanced skincare: Focus on nanodelivery systems. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 79, 104125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.105087
[5] Li, F., Chen, H., Chen, D., Zhang, B., Shi, Q., He, X., & Wang, F. (2023). Clinical evidence of the efficacy and safety of a new multi-peptide anti-aging topical eye serum. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 22(12), 3340–3346. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.15849
[6] Kang, S. M., Joun, Y. S., Lee, K. Y., Kang, H., & Lee, S. G. (2021). Synthesis of tetrapeptide derived from skin structural protein sequence and identification of skin anti-aging effect. Korean Journal of Biomedical Science, 25(4), 56–63. https://doi.org/10.15616/BSL.2021.27.4.231
[7] Fisher, G. J., Talwar, H. S., Lin, J., & Voorhees, J. J. (1999). Molecular mechanisms of photoaging in human skin in vivo and their prevention by all‐trans retinoic acid. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 69(2), 154–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.1999.tb03268.x
[8] Imbert, I., Botto, J. M., Farra, C. D., & Domloge, N. (2012). Modulation of telomere binding proteins: A future area of research for skin protection and anti-aging target. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 11(2), 162–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2165.2012.00611.x
[9] Carrillo Norte, J. A., García Mir, B., Quintana, L., Buracchio, B., & Guerrero Bonmatty, R. (2024). Anti-aging effects of low-molecular-weight collagen peptide supplementation on facial wrinkles and skin hydration: Outcomes from a six-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cosmetics, 11(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11040137
[10] Kalasariya, H. S., Maya Ramírez, C. E., Cotas, J., & Pereira, L. (2024). Cosmeceutical significance of seaweed: A focus on carbohydrates and peptides in skin applications. Phycology, 4(2), 276–313. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology4020015
[11] Zhao, X., Zhang, X., & Liu, D. (2021). Collagen peptides and the related synthetic peptides: A review on improving skin health. Journal of Functional Foods, 82, 104509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2021.104680

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














