Dilemmas and Breakthroughs in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in China
Abstract
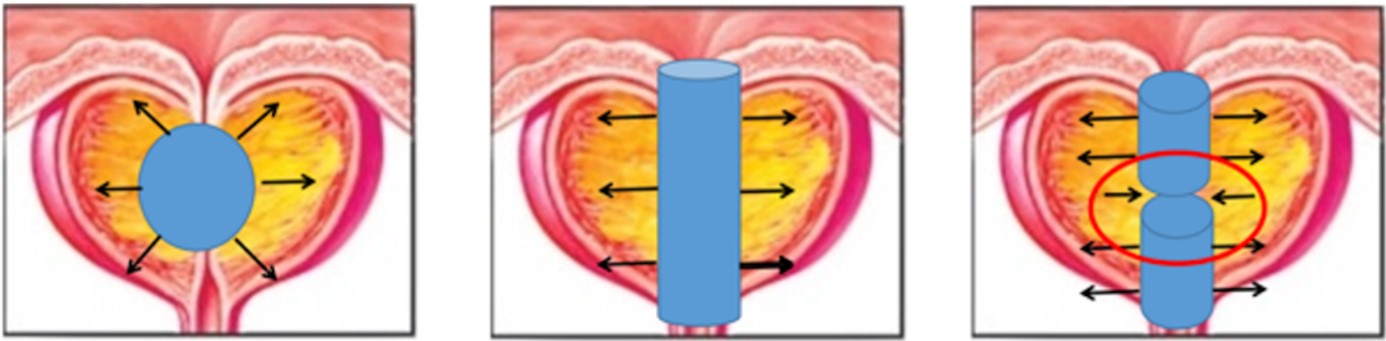
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common urologic disease in elderly men, which seriously affects patients' quality of life. Current treatments mainly include medication and surgery, but both have their own limitations. In recent years, Prostatic Urethral Dilation (PUD), as a new non-resectable mechanical dilatation technique, has gradually become a hot spot for research and clinical application. This article summarizes the current status of BPH treatment in China, the existing dilemmas, and focuses on the technical features and advantages of PUD technology and the latest product, a Ultra-Minimally Invasive Prostate Dilation Catheter (Longevity Bar), with particular attention to its breakthrough in preserving prostate function and reducing postoperative complications, as well as its advantages for high-risk patients based on the innovation of the thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) material and the precise positioning technology of the double balloon. The clinical appropriateness of the TPU material innovation and double balloon precise positioning technology for the elderly and high-risk patient groups, with a view to providing new treatment ideas for the clinic.
References
Bizimana Rukundo, T. (n.d.). The Role of Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation in the Pathogenesis of BPH.
Cannarella, R., Condorelli, R. A., Barbagallo, F., La Vignera, S., & Calogero, A. E. (2021). Endocrinology of the Aging Prostate: Current Concepts. Frontiers in Endocrinology (Lausanne), 12, 554078. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.554078
Carson, C., III, & Rittmaster, R. (2003). The role of dihydrotestosterone in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology, 61(4), 2-7.
Chang, Y., Chang, J., & Wang, H. (2018). Transurethral balloon dilatation of the Prostate and Transurethral Plasmakinetic resection of the Prostate in the treatment of Prostatic Hyperplasia. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, 34(3), 736.
Gu, Y., Xu, Z., Fan, F., Wei, L., Wu, T., & Li, Q. (2023). Highly Breathable, Stretchable, and Tailorable TPU Foam for Flexible Gas Sensors. ACS Sensors, 8(10), 3772-3780. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.3c01204
Gulur, D. M., Mevcha, A. M., & Drake, M. J. (2011). Nocturia as a manifestation of systemic disease. BJU International, 107(5), 702-713.
Hariri, A. R., & Weinberger, D. R. (2003). Imaging genomics. British Medical Bulletin, 65(1), 259-270.
Hoffman, R. M., MacDonald, R., Slaton, J. W., & Wilt, T. J. (2003). Laser prostatectomy versus transurethral resection for treating benign prostatic obstruction: a systematic review. The Journal of Urology, 169(1), 210-215.
Huang, S. W., Tsai, C. Y., Tseng, C. S., Shih, M. C., Yeh, Y. C., Chien, K. L., Pu, Y. S., & Tu, Y. K. (2019). Comparative efficacy and safety of new surgical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ, 367, l5919. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l5919
Huang, W., Guo, Y., Xiao, G., & Qin, X. (2015). Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia using transurethral split of the prostate with a columnar balloon catheter. Journal of Endourology, 29(3), 344-350.
Huang, Y., Li, J., Yang, S., Yuan, D., & Wang, S. (2020). Efficacy and safety of transurethral split of prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a meta-analysis. BMC Urology, 20, 1-11.
Leung, S. K. W., & McNeill, S. A. (2006). Therapeutic Options for Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) and Prostatic Cancer. In Andrology for the Clinician (pp. 535-550).
Madersbacher, S., Marszalek, M., Lackner, J., Berger, P., & Schatzl, G. (2007). The long-term outcome of medical therapy for BPH. European Urology, 51(6), 1522-1533.
Ng, M., Leslie, S. W., & Baradhi, K. M. (2025). Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
Nicholson, T. M. (2015). Estrogen Receptor-alpha is a Key Mediator and Therapeutic Target in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia [University of Rochester].
Rassweiler, J., Teber, D., Kuntz, R., & Hofmann, R. (2006). Complications of transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)--incidence, management, and prevention. European Urology, 50(5), 969-979; discussion 980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.042
Reich, O., & Seitz, M. (2008). [Laser vaporization of the prostate: all as it should be?]. Urologe A, 47(4), 461-462, 464-466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00120-008-1663-z
Taberna, M., Gil Moncayo, F., Jané-Salas, E., Antonio, M., Arribas, L., Vilajosana, E., Peralvez Torres, E., & Mesía, R. (2020). The multidisciplinary team (MDT) approach and quality of care. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 85.
Tsai, S., Thomas, D., Chughtai, B., & Kaplan, S. (2018). Bipolar Plasma Kinetic Vaporization. In A Comprehensive Guide to the Prostate (pp. 47-52). Elsevier.
Wang, W., Guo, Y., Zhang, D., Tian, Y., & Zhang, X. (2015). The prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia in mainland China: evidence from epidemiological surveys. Scientific Reports, 5, 13546. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13546
Wasilewski, T., Kamysz, W., & Gębicki, J. (2024). AI-assisted detection of biomarkers by sensors and biosensors for early diagnosis and monitoring. Biosensors, 14(7), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14070356

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














