Studies on the Lipid Profiles of Wistar Rat Models Treated with Aqueous and Methanolic Leaf Extracts of Alchornea Cordifolia and Thaumatococcus Daniellii
Abstract
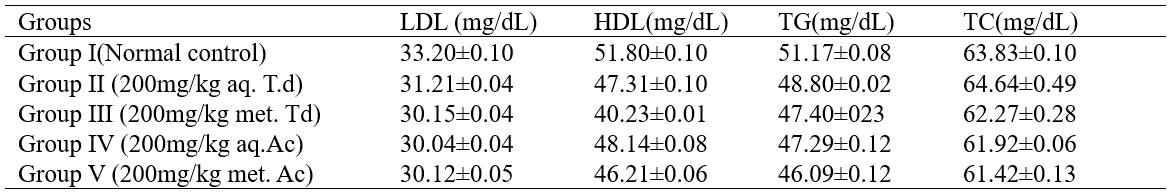
This study aims at establishing the effect of T. daniellii and A. cordifolia leaf extracts on the lipid profile of experimental rat models. A total of twenty five (25) adult male wistar rats were used for the study. The rats were divided into five groups of five rats each. Group I (normal control) was administered with 2ml/kg distilled water p.o. Group II was administered with 200mg/kg aqueous leaf extract of T. daniellii p.o. Group III was administered with 200mg/kg methanolic leaf extract of T. daniellii p.o. Group IV and V were administered with 200mg/kg aqueous and methanolic leaf extracts of A. cordifolia respectively. Administration of extracts lasted for 14 days after which animals were sacrificed and serum developed from blood samples was collected and used for analysis to evaluate the lipid profiles of experimental models using standard methods. Results obtained from the study show that the highest level of Low Density Lippoprotein (LDL) (31.21±0.04 mg/dL) was recorded on Group II and was not significantly different from the control group (33.20±0.10 mg/dL). However, for High Density Lipoprotein (HDL), the highest level was recorded on Group IV (48.14±0.08mg/dL). Similarly, this was not significantly different from the Control group (51.80±0.10mg/dL). Group II presented the highest level of Triacylglyceride (TG) (48.80±0.02mg/dL), which however, was considered not significantly different from the control group (51.17±0.08mg/dL). For Total Cholesterol (TC), highest level (64.64±0.49mg/dL) was recorded on Group II and value was not significantly different from that recorded on the normal control (63.83±0.10mg/dL). In conclusion, it can be deduced from this study that extracts of T. daniellii and A. cordifolia lacks the potential to alter the lipid profile of patients depending on them for one medicinal use or the other and may thus be considered potential candidates for drug development.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














