A Comprehensive Review of Chinese Herbal Formulations for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
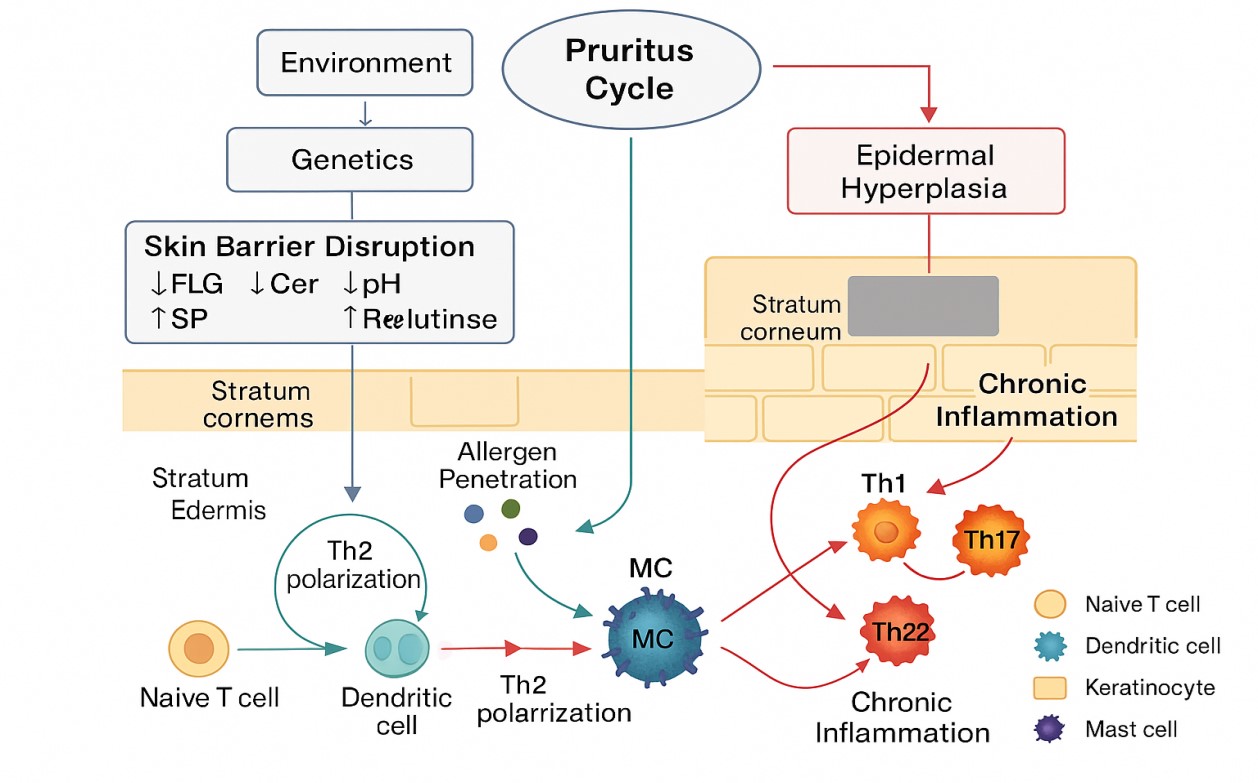
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common, chronic, and relapsing inflammatory skin disorder characterized by skin irritation and intense pruritus, which significantly impairs the quality of patients’ life. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a long history in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, especially in preventing disease recurrence, minimizing adverse reactions and alleviating disease burden. In this paper, we reviewed the clinical anti-AD efficacy of Chinese herbal formulae from the perspective of AD mechanisms. Following assessment indicators were used: SCORing Atopic Dermatitis (SCORAD), erythema intensity, skin quality of life index (DLQI), pruritus intensity and frequency, transdermal dehydration (TEWL), and AD-mediated chemokine expression levels as index formulae. We also summarize the pharmacological effects of single herbs in the formulae. In conclusion, TCM has significant clinical efficacy for patients of all ages, both as a standalone treatment and in combination with other therapies.
References
[2] Rodriguez, E., Baurecht, H., Herberich, E., Wagenpfeil, S., Brown, S. J., Cordell, H. J., Thyssen, J. P., Reingruber, J., Schreiber, S., Lee, Y. A., & Weidinger, S. (2009). Meta-analysis of filaggrin polymorphisms in eczema and asthma: Robust risk factors in atopic disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 123(6), 1361–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.03.036
[3] Dillon, S. R., Sprecher, C., Hammond, A., Bilsborough, J., & Shea, D. (2005). Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice (vol 5, pg 752, 2004). Nature Immunology, 6(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0105-114a
[4] Dubin, C., Del Duca, E., & Guttman-Yassky, E. (2021). The IL-4, IL-13 and IL-31 pathways in atopic dermatitis. Expert Review of Clinical Immunology, 17(8), 835–852. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2021.1940962
[5] Jo, G. H., Kim, S. N., Kim, M. J., Cho, M., Kim, S. B., Ahn, Y. W., Kim, J., Kim, S. H., Park, J. H., Kim, M., Hong, S. H., Park, C. K., & Shim, I. (2018). Protective effect of Paeoniae radix alba root extract on immune alterations in mice with atopic dermatitis. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health-Part a-Current Issues, 81(12), 502–511. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2018.1460785
[6] Liu, J., Mo, X., Wu, D., Li, Y., Liang, M., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Gao, D. (2015). Efficacy of a Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: A randomised controlled study. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 23(5), 644–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2015.07.006
[7] Lin, Y. K., Chang, S. H., Yang, C. Y., Wang, C. Y., Chen, W. Y., Lin, Y. M., & Hsieh, S. C. (2020). Efficacy and safety of indigo naturalis ointment in Treating Atopic Dermatitis: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 250, 112477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112477
[8] Li, Y. Q., Shen, T. T., Wang, Q. Y., Zhao, M., Xu, F., Guo, Z., Chen, G. B., Zhao, H. T., Li, M. G., Yang, Z. R., & Wang, Q. (2022). The efficacy and safety of Longmu Tang granule for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: study protocol for a single-centred, double-blinded, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Trials, 23(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-022-06313-w
[9] Lin, J. F., Liu, P. H., Huang, T. P., Hsueh, J. H., Sun, C. C., Chen, S. J., & Chang, Y. F. (2014). Characteristics and prescription patterns of traditional Chinese medicine in atopic dermatitis patients: Ten-year experiences at a Medical Center in Taiwan. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 22(1), 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2013.12.003
[10] Lee, J., Choi, Y. Y., Kim, M. H., Kim, M., & Kim, Y. J. (2016). Topical Application of Angelica sinensis Improves Pruritus and Skin Inflammation in Mice with Atopic Dermatitis-Like Symptoms. Journal of Medicinal Food, 19(1), 98–105. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2015.3489
[11] Cheng, H. M., Chiang, L. C., Jan, Y. M., Yen, M. H., & Lin, C. C. (2011). The Efficacy and Safety of a Chinese Herbal Product (Xiao-Feng-San) for the Treatment of Refractory Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology, 155(2), 141–148. https://doi.org/10.1159/000318861
[12] Sheehan, M. P., & Atherton, D. J. (1992). A CONTROLLED TRIAL OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINAL-PLANTS IN WIDESPREAD NON-EXUDATIVE ATOPIC ECZEMA. British Journal of Dermatology, 126(2), 179–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb07817.x
[13] Kang, S. J., Cho, H. B., Jo, E. H., An, M. W., Park, J. H., Han, G., Yoon, J., Kim, K. S., & Kim, M. J. (2020). Efficacy and safety of So-Cheong-Ryong-Tang in patients with atopic dermatitis and respiratory disorders Study protocol of a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Medicine, 99(2), 18565. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018565
[14] Kim, K. H., Kwun, M. J., Choi, J. Y., & Lee, S. H. (2013). Therapeutic Effect of the Tuber of Alisma orientale on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2013, 863892. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/863892
[15] Salameh, F., Perla, D., Solomon, M., Ziv, M., & Zadik, M. (2008). The Effectiveness of Combined Chinese Herbal Medicine and Acupuncture in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 14(8), 1043–1048. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0162

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














