Effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction on Platelet Related Biological Indexes in Pulmonary Fibrosis Model Rats
Abstract
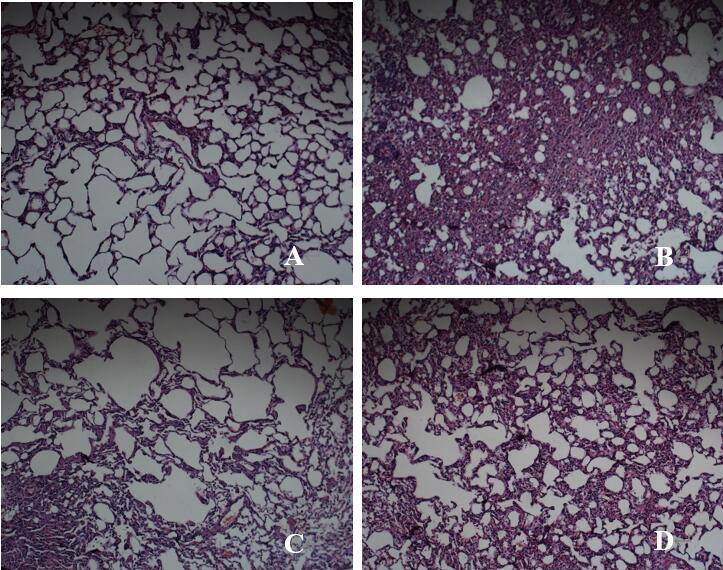
Objective: Taking Bu Yang Huan Wu Decoction as the research object, a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis was replicated to study the changes in platelets during the development of pulmonary fibrosis, providing a certain research basis for the clinical application of Bu Yang Huan Wu Decoction to alleviate the pathological state of pulmonary fibrosis. Research Method: The animals selected by this experiment are SD rats, which are randomly divided into blank groups, model groups, and complement (14.0g/kg) and low-low groups (3.5g/kg). The pelvic fibrosis rats were obtained in the bronchus injection of bolithycin solution (7mg/kg). After the continuous molding 21 d, the rats were continuously administered for 14 d. After the last time it was administered for 1 H, the abdominal aortic blood was taken to take blood, and the relevant testing indicators were continued. Research Results: Compared with the blank group, the blood viscosity of the rats in this group is significantly higher under the variable variable transmission in the full blood viscosity, and the viscosity of low -cut blood is significantly increased, and the viscosity of the plasma also increased significantly; the content of platelet indicators VWF,FN, β-TG, and PF4 all increased significantly. Related parameters have significantly elevated PLT, MPV,PCT,PDW, PLCR are significantly increased ; the PT content of coagulation parameters is significantly reduced, and the increase in FIB content is significant; The content of inflammation factor parameters TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 increased significantly, and the IL-10 content was significantly reduced. Compared with the model group, the high-dose group significantly reduces the full blood viscosity of low, medium and high-cut, and plasma viscosity is significantly reduced; platelet indicators FN, β-TG,VWF and PF4 are decreased significantly; related parameters PLT, MPV, PCT, PDW, PLCR are all significantly reduced; significantly increased coagulation parameter PT content, significantly reduced the FIB content ; IL-1β, IL-17, TNF-α have decreased significantly, significantly increased IL-10 content; The whole blood viscosity under the variable rate has significantly reduced effect, and the plasma viscosity is significantly reduced. A significant reduction of platelet indicators VWF, FN, β-TG, PF4 content, the t-PA content is significantly increased; MPV and PLCR have decreased significantly, which is significantly reduced by significant reduction PLT, PDW, PCT; significantly increased PT content of coagulation parameters, significantly reduced the FIB content ; Reduce , the IL-10 content increases significantly. Conclusion: 1) Bleomycin replicated pulmonary fibrosis model can cause abnormal changes in hemorheology; Abnormal changes of platelet parameters; 2) Buyang Huanwu Decoction improved the blood stasis level of pulmonary fibrosis, reduced blood viscosity and platelet parameters, inhibited the release of inflammatory factors, and alleviated the pathological state of lung tissue in pulmonary fibrosis.
References
[2] Zhang, J. B., Chen, P. P., et al. (2022). Effects of different proportions of Baicalein-red peony drugs on rat liver fibrosis model. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary, 28(12), 69–77.
[3] Wang, L. J., Dong, X. P., & Tu, T. (2021). Effects of Angelica sinensis and Chuangxiong on TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in pulmonary fibrosis model rats. Chinese Patent Materia Medica, 43(6), 1451–1456.
[4] Yang, H., Wang, F., Yang, K., et al. (2017). Effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction on the expression of ERK in lung tissue of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis rats. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 32(4), 1727–1730.
[5] Boren, E., & Gershwin, M. E. (2004). Inflamm-aging; autoimmunity, and the immune-risk phenotype. Autoimmunity Reviews, 3(5), 401–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2004.03.004
[6] Culleton, B. F., Larson, M. G., Kannel, W. B., et al. (1999). Serum uric acid and risk for cardiovascular disease and death: The Framingham Heart Study. Annals of Internal Medicine, 131(1), 7–13. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-131-1-199907060-00003
[7] Eleonore, F. (2016). Action of nanoparticles on platelet activation and plasmatic coagulation. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 23(5), 408–430. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160106151428
[8] Anselmo, A. C., Modery-Pawlowski, C. L., Menegatti, S., Kumar, S., Vogus, D. R., Tian, L. L., Chen, M., Squires, T. M., & Mitragotri, S. (2014). Platelet-like nanoparticles: Mimicking shape, flexibility, and surface biology of platelets to target vascular injuries. ACS Nano, 8(11), 11243–11253. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn503732m
[9] Senis, Y. A., Mazharian, A., & Mori, J. (2014). Src family kinases: At the forefront of platelet activation. Blood, 124(13), 1123–1153. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-01-453134
[10] Vogel, S., & Thein, S. L. (2018). Platelets at the crossroads of thrombosis, inflammation and haemolysis. British Journal of Haematology, 180(5), 2085–2092. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.15117
[11] Nandi, S., Sproul, E. P., Nellenbach, K., et al. (2019). Platelet-like particles dynamically stiffen fibrin matrices and improve wound healing outcomes. Biomaterials Science, 7(4), 2135–2164. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8BM01201F
[12] Lopez, E., Srivastava, A. K., Burchfield, J., et al. (2019). Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles promote hemostasis and prevent the development of hemorrhagic shock. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 2305–2315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53724-y
[13] French, S. L., Butov, K. R., Allaeys, I., et al. (2020). Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles infiltrate and modify the bone marrow during inflammation. Blood Advances, 4(13), 3011–3023. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001758
[14] Lei, Q., Gu, H., Li, L., et al. (2020). TNIP1-mediated TNF-α signalling cascade sustains glioma cell proliferation. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(1), 530–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14760
[15] Bian, J. Q., Niu, W. Y., et al. (2020). Effect of Buyang Huanwu Decoction on platelet activation in Qi deficiency and blood stasis model. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 22(2), 43–46.
[16] Maher, T. M., Corte, T. J., Fischer, A., et al. (2020). Pirfenidone in patients with unclassifiable progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 8(2), 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30341-8

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














