Rapid UPLC-MS/MS Determination of Amantadine and Rimantadine in Human Blood and Urine for Forensic Toxicology
Abstract
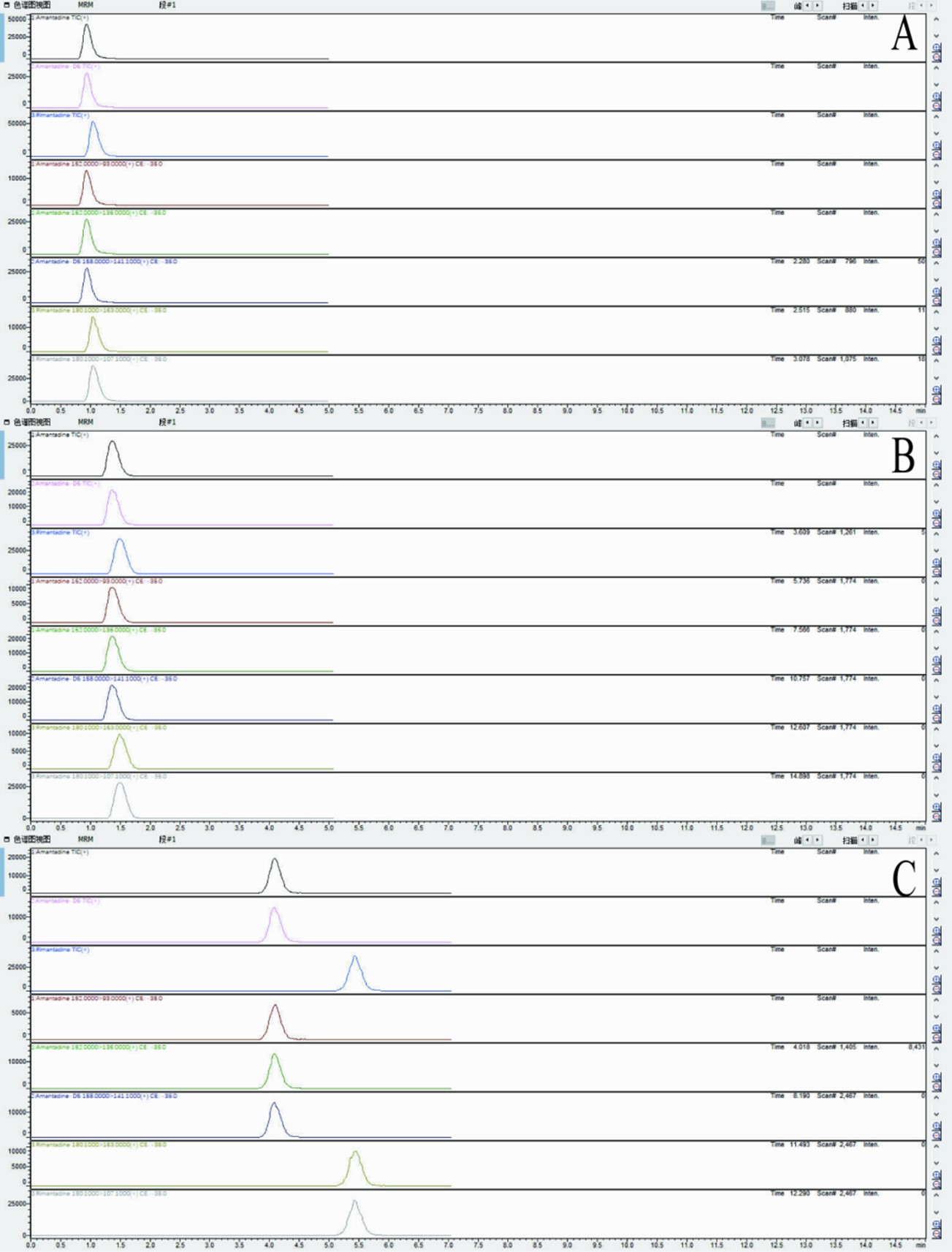
A rapid UPLC-MS/MS method was developed and validated for quantifying amantadine (AMD) and rimantadine (RIM) in human blood and urine. Sample preparation involved acetonitrile protein precipitation with amantadine-D6 as internal standard. Separation used an ACE C₁₈-PFP column and a mobile phase of 0.1% aqueous formic acid/5 mmol/L ammonium formate-acetonitrile (85:15, v/v). ESI⁺-MRM detection was employed. Acetonitrile provided optimal extraction. The method showed excellent linearity (1.0–1000.0 ng/mL; R² > 0.99), LOD/LOQ , mean recoveries (82.16–105.43%), and precision (RSD 3.57–10.39%). This sensitive, reliable method is suitable for forensic and public health applications.
References
[2] Dong, G., Peng, C., Luo, J., Wang, C., Han, L., Wu, B., Ji, G., & He, H. (2015, March 13). Adamantane-resistant influenza A viruses in the world (1902–2013): Frequency and distribution of M2 gene mutations. PLoS One, 10(3), e0119115. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119115
[3] Gros-Louis, P., Charest, S., & Légaré, M. E. (2021, August). Late-onset bilateral epithelial ingrowth following rapid corneal decompensation owing to amantadine. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology, 56(4), e137–e139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjo.2021.02.019
[4] Vale, J. A., & Maclean, K. S. (1977, March 5). Amantadine-induced heart failure. Lancet, 1(8010), 548. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(77)91411-8
[5] Schwartz, M., Patel, M., Kazzi, Z., & Morgan, B. (2008, September). Cardiotoxicity after massive amantadine overdose. Medical Toxicology, 4(3), 173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03161197
[6] Cook, P. E., Dermer, S. W., & McGurk, T. (1986, November). Fatal overdose with amantadine. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 31(8), 757–758. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674378603100814
[7] Xu, Y., Ren, C., Han, D., Gong, X., Zhang, X., Huang, H., Jiang, F., Cui, Y., Zheng, W., & Tian, X. (2019, September 15). Analysis of amantadine in Laminaria Japonica and seawater of Daqin Island by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with positive electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 1126–1127, 121697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.06.024
[8] Wang, Z., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Wu, C., & Zhou, J. (2021, February 8). Simultaneous determination of five antiviral drug residues and stability studies in honey using a two-step fraction capture coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1638, 461890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.461890
[9] Ho, C., & Wong, Y. T. (2014, July–August). Fast and high throughput screening of amantadine in chicken muscle by extractive derivatization with pentafluorobenzoyl chloride and gas chromatography/negative ion chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of AOAC International, 97(4), 1220–1224. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.13-245

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








1.png)














