Research on Influencing Factors of College Students' Willingness to Use Mobile Learning
Abstract
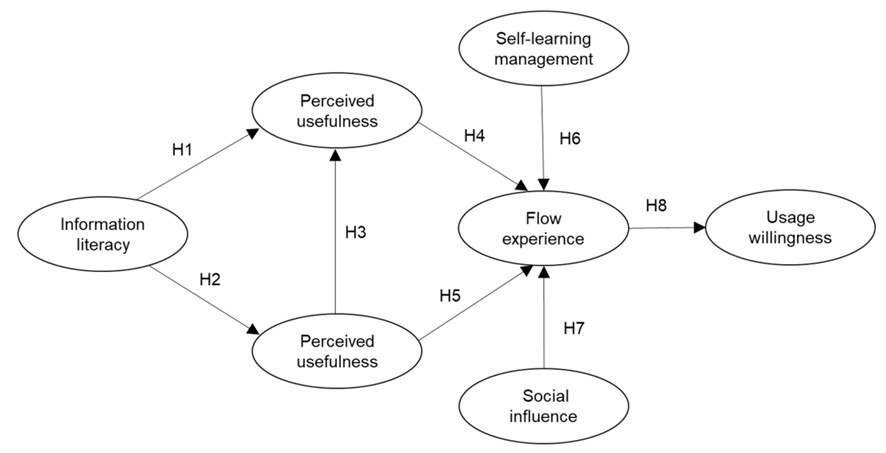
As a new way of learning, mobile learning is no longer limited by time and space. College students, the main audience group of mobile learning, study the factors that affect college students' willingness to use mobile learning is helpful to improve their motivation for mobile learning. Therefore, based on the theory of technology acceptance model, information literacy theory, self-management theory, and social influence theory, this study designed a questionnaire on factors influencing college students' willingness to use mobile learning by taking variables such as information literacy, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, self-learning management, social influence, and flow experience as dimensions. In this paper, 535 students at Hubei University of Medicine were investigated, and structural equation model analysis was used to verify the theoretical model and discuss the effect relationship among the variables. The results proved that information literacy has a positive impact on perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness; perceived ease of use has a positive effect on perceived usefulness; perceived usefulness, self-learning management, and social influence had positive effects on immersion experience.
References
[2] Zhang, S.-J. (2017). Mobile learning model and process optimization in the era of fragmentation. EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 13(7), 3641–3652. https://doi.org/10.12973/eurasia.2017.00750a
[3] Huang, R., & Salomaa, J. (2008). Mobile Learning: Theory, Current Situation and Trends. Beijing: Science Press.
[4] Demir, K., & Akpınar, E. (2018). The effect of mobile learning applications on students' academic achievement and attitudes toward mobile learning. The Malaysian Online Journal of Educational Technology, 6, 48–59. https://doi.org/10.17220/mojet.2018.02.004
[5] Al Emran, M. (2020). Mobile learning during the era of COVID 19. 2020. https://doi.org/10.35575/rvucn.n61a1
[6] Alsswey, A., & Al Samarraie, H. (2019). M-learning adoption in the Arab Gulf countries: A systematic review of factors and challenges. Education and Information Technologies, 24(5), 3163–3176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-019-09923-1
[7] He, H., & Zhang, H. (2019). Analysis of influencing factors of college students' English mobile learning behavior based on UTAUT model. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology (Philosophy & Social Sciences Edition), 36(05), 73–79.
[8] Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1989). User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science, 35(8), 982–1003. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.35.8.982
[9] Wong, T. K. M., Man, S. S., & Chan, A. H. S. (2021). Exploring the acceptance of PPE by construction workers: An extension of the technology acceptance model with safety management practices and safety consciousness. Safety Science, 139, 105239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2021.105239
[10] Gao, H., Xing, Z., & Zhao, D. (2021). Influencing factors of college students' knowledge acquisition behavior from the perspective of information literacy. Intelligence Science, 39(08), 37–43.
[11] Kelman, H. C. (1958). Compliance, identification, and internalization: Three processes of attitude change. Journal of Conflict Resolution, 2, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/002200275800200106
[12] Wei, M. (2018). A study on the factor model of college students' willingness to use mobile learning [Master’s thesis, Central University for Nationalities].
[13] Kuang, Y., Liang, Z., & Yang, Y. (2021). Research on the influencing factors of flipped classroom acceptance among higher vocational and technical college students. Journal of Guilin Normal University of Higher Vocational Education, 35(05), 83–90.
[14] Xu, S., & Tian, X. (2020). Research on the influencing factors of users' willingness to use online learning platforms based on TAM. China Education Informatization, (08), 78–85.
[15] Kelly. (2022). Factors influencing virtual simulation learning experiences and their correlation: A case study of the virtual simulation experiment on handling sudden safety incidents in primary and secondary school classrooms. China Education Informatization, 28(03), 106–112.
[16] Hsu, C.-L., & Lu, H.-P. (2004). Why do people play online games? An extended TAM with social influences and flow experience. Information & Management, 41(7), 853–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2003.08.014
[17] Chen, L. (2018). Factors influencing the willingness of mobile live broadcast users to pay: A perspective based on the theory of immersion. Southeast Communication, (10), 98–101.
[18] Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18, 39–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/3150980
[19] Tsai, T.-H., Chang, H.-T., Chang, Y.-C., & Chang, Y.-S. (2017). Personality disclosure on social network sites: An empirical examination of differences in Facebook usage behavior, profile contents and privacy settings. Computers in Human Behavior, 76, 469–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.08.003
[20] A. B. K. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. John Wiley & Sons.
[21] Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling.
[22] Wu, G. (2014). Analysis of influencing factors of college students' mobile learning based on TAM model [Master’s thesis, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications].
[23] Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). Play and intrinsic rewards. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology: The collected works of Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi (pp. 135–153). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9088-8_10
[24] Wang, H., Ding, J., Akram, U., Yue, X., & Chen, Y. (2021). An empirical study on the impact of e-commerce live features on consumers’ purchase intention: From the perspective of flow experience and social presence. Information, 12(8), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12080324
[25] Wang, Y.-S., Wu, M.-C., & Wang, H.-Y. (2009). Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 40, 92–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2007.00809.x
[26] Dong, Y. (2020). An empirical study on mobile learning of college English vocabulary. China Metallurgical Education, (03), 33–35.
[27] Zhang, H. (2021). A study on the continuous use willingness of college students to online teaching platforms. China Education Informatization, (22), 7–13.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














