Culturally Important Objects as Signs of Cretan Protolinear Script
Abstract
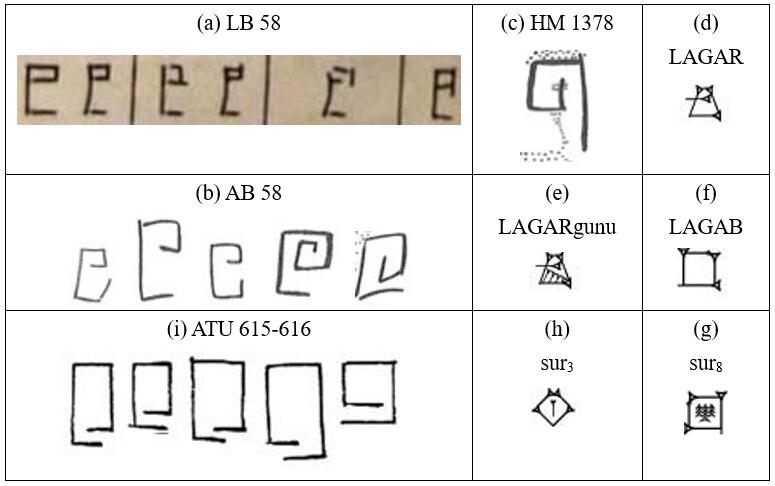
This paper presents seven “syllabograms” of the Cretan Protolinear script (signs used for Consonant-Vowel [CV] syllables). This presentation is conducted following the theory of the Cretan Protolinear (CP) script as the one that all the Aegean scripts evolved from, including Linear A, Cretan Hieroglyphics and Linear B. The seven syllabograms of this particular set depict inanimate objects or constructions that were very common or important in everyday life, economy and religion. It is also demonstrated that the phonetic value of each syllabogram corresponds to the Sumerian name of the object depicted by the syllabogram, in a conservative dialect. Thus, more light is shed on the linguistic ancestry of the Aegean scripts, the practice followed for their creation, and, indirectly, on some cultural aspects of the Minoan Civilization.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














