Challenges and Pathways for the Aging Neighborhood Renovation from the Perspective of Participatory Governance: A Case Study of X Community in H Street, Yinchuan City
Abstract
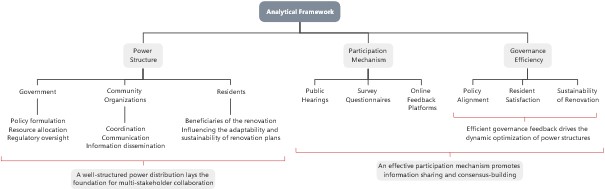
The renovation of aging neighborhoods faces challenges such as governance imbalance and insufficient resident participation, leading to low renovation efficiency. Based on the theory of participatory governance, this paper constructs an analytical framework of "power structure—participation mechanism—governance efficiency" to reveal the causes of dilemmas in the renovation cases of coal sheds and markets in X Community, H Street. The government-led "power structure imbalance" marginalizes residents' demands, the "breakdown of formalized participation mechanisms" exacerbates negotiation failures, and conflicts of diverse interests lead to the "dissipation of governance efficiency." To address these challenges, this study proposes a four-dimensional optimization strategy: adopting differentiated renovation strategies to balance safety concerns and resident needs, establishing a clear legal framework to clarify property rights, building institutionalized consultation platforms to strengthen residents’ decision-making power, and promoting community cultural integration to enhance collective recognition. By reconstructing the governance logic of "government-community-residents" co-governance, this study promotes the shift of residents from symbolic participation to substantive decision-making, providing a new paradigm for resolving conflicts of interest and implementation obstacles in aging neighborhood renovation, thereby contributing to the modernization of grassroots governance.
References
[2] Hu, Z., Li, Z., & Li, L. (2025). Research on the long-term operation mechanism of old residential areas from the perspective of scale reconstruction: Empirical study of Wuhan's "property city" model. Journal of Natural Resources, 40(1), 134–146. https://doi.org/10.5678/jnr.2025.002
[3] Junda, Huang, Y., & Guo, G. (2024). Research on the utilization of solar energy in the renovation of multi-storey old residential buildings in Shanghai. Architectural Journal, (S2), 136–141. https://doi.org/10.9101/arch.2024.s2.003
[4] Zhang, R., Kong, D., & Li, H. (2024). The aging renovation strategy of old communities under the community home care model. Planner, 40(S2), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.1123/plan.2024.s2.004
[5] Wu, J., & Guo, C. (2024). Emotional embedding, interest coordination and renovation of old communities: A case study of elevator installation in Hemu Village. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), (6), 85–96, 171. https://doi.org/10.3345/jfnu.2024.005
[6] Liang, Y., Qian, Q. K., Li, B., & et al. (2025). A critical assessment on China's old neighborhood renovation: Barriers analysis, solutions and future research prospects. Energy & Buildings, 332, 115407. https://doi.org/10.6789/eb.2025.006
[7] Peng, W., Huang, Y., Li, C., & et al. (2025). Exploration of resident satisfaction and willingness in the renovation of a typical old neighborhood. Buildings, 15(2), 293. https://doi.org/10.1016/build.2025.007
[8] Ran, O. (2024). Reconstruction of old communities from the perspective of grassroots governance: Practical forms and theoretical framework. Journal of Yunnan Minzu University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 41(2), 90–97. https://doi.org/10.2134/ymu.2024.008
[9] Que, Y. (2024). Research on the index system of old neighborhood renovation based on green building evaluation standard. Journal of Architectural Research and Development, 8(3), 140–146. https://doi.org/10.4156/jard.2024.009
[10] Li, W., Li, Q., & Li, Y. (2023). Decision-making factors for renovation of old residential areas in Chinese cities under the concept of sustainable development. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 30(14), 39695–39707. https://doi.org/10.1007/espr.2023.010
[11] Sun, G., Tang, X., Wan, S., & et al. (2022). An extended fuzzy-DEMATEL system for factor analyses on social capital selection in the renovation of old residential communities. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 134(2), 1041–1067. https://doi.org/10.3267/cmes.2022.011
[12] Luo, X., Ren, M., Zhao, J., & et al. (2022). Life cycle assessment for carbon emission impact analysis for the renovation of old residential areas. Journal of Cleaner Production, 367, 132930. https://doi.org/10.1016/jclepro.2022.012
[13] Yan, S., & Zhang, P. (2022). Research on the application of a new type of trash can in the renovation of old communities. Journal of Sociology and Ethnology, 4(4), 13–16. https://doi.org/10.7890/jse.2022.013
[14] Dai, X., & Lin, B. (2024). The practice pattern and operation and maintenance path of stock resource renovation in old residential areas: An analysis framework based on dynamic capability theory. Learning and Practice, (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.2345/lp.2024.014
[15] Zhao, N., & Liu, Y. (2023). Analysis of policy evolution and planning effectiveness of old community renovation from the perspective of "structure-activity" policy tools. Urban Development Research, 30(11), 75–82. https://doi.org/10.5678/udr.2023.015
[16] Li, X., & Huang, M. (2020). Evaluation of the old residential area modification by applying improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 467(1), 012189. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/467/1/012189
[17] Zhang, D., & Zhao, Y. (2023). Responsibility connection: Mechanism shaping and practice approach of community governance community operation—Case comparison based on the aging neighborhood renovation. Fact, (6), 65–78, 109. https://doi.org/10.9012/fact.2023.017
[18] Guo, Y., Wang, H., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Research on the formation mechanism and renewal governance model of informal space in old residential areas: Taking Wuhan as an example. Urban Planning Journal, (5), 103–109. https://doi.org/10.3456/upj.2023.018
[19] Li, Y., Liu, X., & Yu, P. (2023). Constructive renovation path of urban community conflict under the concept of flexibility: A case study based on the aging neighborhood renovation in City A. Urban Development Research, 30(8), 126–132. https://doi.org/10.5678/udr.2023.019
[20] Kou, H., & Du, P. (2023). The logic, strategy and path of aging renovation in old communities. Beijing Social Sciences, (7), 118–128. https://doi.org/10.7890/bss.2023.020
[21] Zhao, Z. (2023). Energy-saving smart city: An edge computing-based renovation and upgrading scheme for old residential areas. International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology, 71(3), 251–257. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijcat.2023.021

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).









1.png)














