The Effect of Three Different Concentrations of a Bio-Stimulant on Lettuce Yield and Quality Variation in NFT System
Abstract
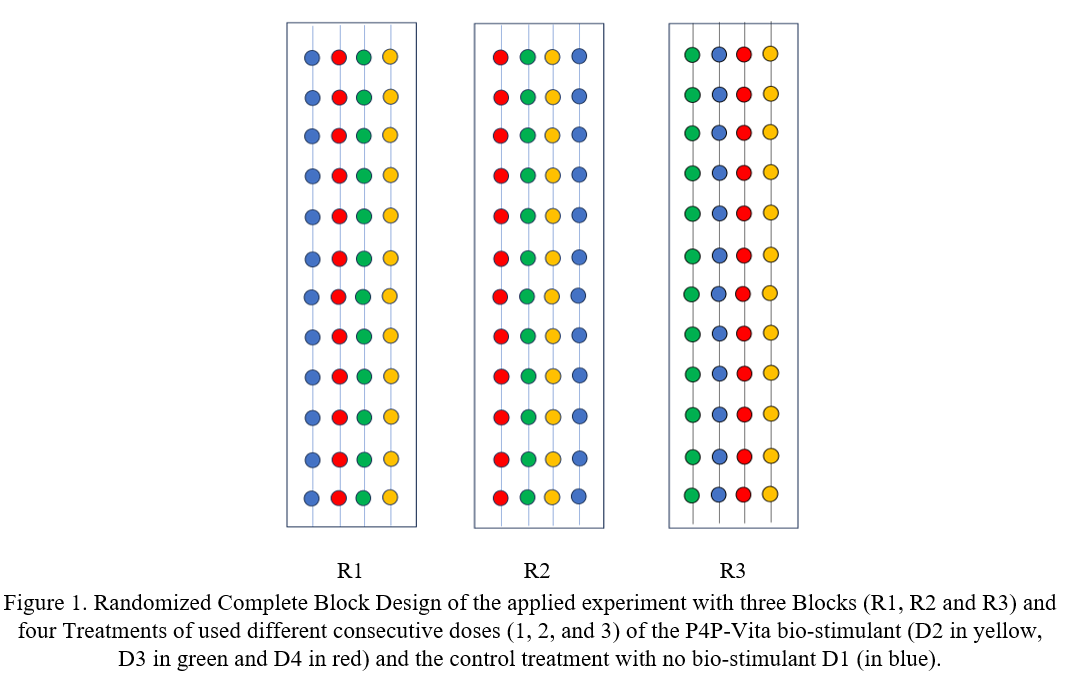
This study examines the impact of three different doses (D2: 0.675 mL/week; D3: 3.375 mL/week; D4: 13.5 mL/week) of a bio-stimulant (P4P-Vita), provided by Van Iperen, on lettuce yield and quality variation in a Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) system. The study compared these doses to a control group (D1) and evaluated the most effective dose for maximizing yield and quality. Parameters such as fresh weight, leaf number, leaf size (length and width), and root system volume were measured on day 0, day of harvest to assess productivity. Additionally, weight loss, Brix degree, and pH were measured on post-harvest days: (0,4,7 and 14) during refrigerated storage to assess quality variation. Results indicate that the bio-stimulant positively influenced lettuce growth and storage. The moderate dose (D2) yielded the best results, promoting higher fresh weight, longer and wider leaves, a more developed root system, reduced weight loss, longer shelf life and improved taste compared to other treatments.
References
Albrecht, U. (2019). Plant biostimulants: Definition and overview of categories and effects. EDIS, 2019(3). https://doi.org/10.32473/edis-hs1330-2019
Alemu, T. T., & Kim, T. (2024). Effect of maturity stages on the quality of cold storage iceberg lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. capitate) for export. Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 7(1), 2052–2063. https://doi.org/10.31817/vjas.2024.7.1.04
Al-Karaki, G. N., & Othman, Y. (2023). Effect of foliar application of amino acids biostimulants on growth, macronutrient, total phenols contents and antioxidant activity of soilless grown lettuce cultivars. South African Journal of Botany, 154, 225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2023.01.034
Araújo, W. F., Tagianne, K., de V., Moreira, B., Barros, M. M., & Estênia Marcolino. (2016). Resposta da alface a adubação nitrogenada. Revista Agro Mbiente On-Line, 5(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.18227/1982-8470ragro.v5i1.440
Aroucha, E. M., Souza, C. L., Aroucha, M. C., & Vianni, R. (2015, December 23). Características físicas e químicas da agua de coco anão verde e anão vermelho em diferentes estádios de maturação. Caatinga, 18(2), 82–87.
Balaguera-López, H. E., Martínez-Cárdenas, C. A., & Herrera-Arévalo, A. (2016). Effect of the maturity stage on the postharvest behavior of cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana L.) fruits stored at room temperature. Bioagro, 28(2), 117–124. Retrieved from http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1316-33612016000200006
Brown, S. K., & Bourne, M. C. (2002). Assessment of components of fruit firmness in selected sweet cherry genotypes. HortScience, 23(5), 902–904. Retrieved from https://eurekamag.com/research/001/760/001760004.php
Bulgari, R., Trivellini, A., & Ferrante, A. (2019). Effects of two doses of organic extract-based biostimulant on greenhouse lettuce grown under increasing NaCl concentrations. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01870
Candido, V., Campanelli, G., D’Addabbo, T., Castronuovo, D., Perniola, M., & Camele, I. (2015). Growth and yield promoting effect of artificial mycorrhization on field tomato at different irrigation regimes. Scientia Horticulturae, 187, 35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.02.033
Chaski, C., & Barros, L. (2022). The effects of biostimulant application on growth parameters of lettuce plants grown under deficit irrigation conditions. IECHo 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecho2022-12499
Chebil, L., Ammar, I. B., Ktari, L., Cherif, D., Cherif, H., & Sadok, S. (2019). Effet de l’extrait liquide de l’algue verte Chaetomorpha linum (Müller) Kütz., 1849 sur la germination et la croissance du blé dur Triticum turgidum L. subsp. Durum. INSTM Bulletin: Marine and Freshwater Sciences, 46, 133–145. Retrieved from https://www.instm-bulletin.tn/index.php/bulletin/article/view/212
Chitarra, A. B., & Chitarra, M. I. F. (2005). Post-harvesting of fruits and vegetables: Physiology and handling (2nd ed., p. 785). Lavras: FAEPE.
Colla, G., Hoagland, L., Ruzzi, M., Cardarelli, M., Bonini, P., Canaguier, R., & Rouphael, Y. (2017). Biostimulant action of protein hydrolysates: Unraveling their effects on plant physiology and microbiome. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02202
Colla, G., Raimondi, G., Di Stasio, E., Cardarelli, M., Bonini, P., Vitaglione, P., & Rouphael, Y. (2019). An endophytic fungi-based biostimulant modulated lettuce yield, physiological and functional quality responses to both moderate and severe water limitation. Scientia Horticulturae, 256, 108595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108595
Desoky, E.-S. M., Elrys, A. S., Mansour, E., Eid, R. M. H. M., Selem, E., Rady, M. M., & Semida, W. M. (2021). Application of biostimulants promotes growth and productivity by fortifying the antioxidant machinery and suppressing oxidative stress in faba bean under various abiotic stresses. Scientia Horticulturae, 288, 110340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110340

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
























