Exploring the Pricing Strategy of Insurance in China Based on the TOPSIS Method
Abstract
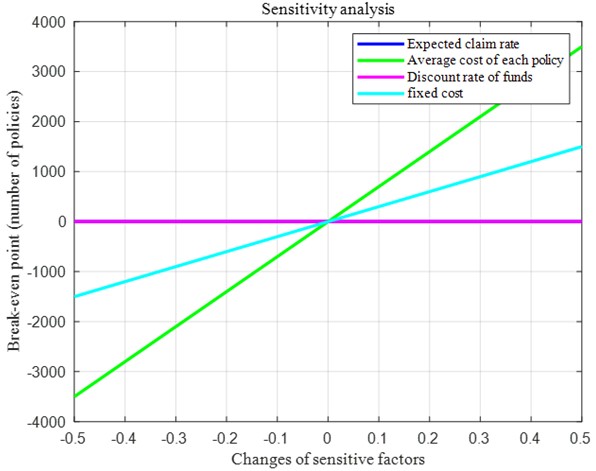
This paper is based on the panel data of extreme weather in China from 2000 to 2023. Firstly, the TOPSIS method is adopted to determine the weights of various indicators affecting the underwriting of insurance companies and establish a risk assessment system. Secondly, the break-even method is used to formulate the premium pricing strategy, and sensitivity analysis is conducted to test the sensitivity of each indicator. Further analysis is carried out to determine when and where the insurance company's underwriting risk is the lowest and the return is the highest. Finally, from the perspective of developers, the model is optimized. Based on the exploration of the influencing factors of building disaster resistance, the disaster resistance coefficient of disaster-resistant buildings is considered to establish a community disaster resistance capacity system model. Developers can determine whether to develop based on the local disaster resistance capacity indicators and the disaster resistance coefficient of disaster-resistant buildings.
References
[2] Yang, S. T., & Li, S. W. (2023). Research on the Impact of Climate Risk on Insurance Demand in China. Financial Review, 15(2), 91-117, 126.
[3] Yu, X. F., & Fu, D. (2004). An overview of multi-indicator comprehensive evaluation methods. Statistics and Decision Making, (11), 119-121.
[4] Ma, Z. Y., & Song, Y. J. (2023). Impact of climate change on financial stability: a theoretical explanation. Southern Finance, (3), 19-36.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).