Instrument for Testing Organizational Citizenship Behavior among University Lecturers in Nigeria: A Pilot Study
Abstract
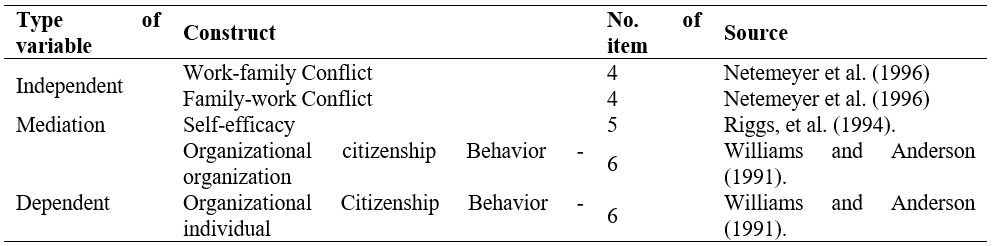
This report is centered upon a pilot research carried out to assess, from a methodological perspective, the mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between work-family conflict, family-work conflict and organizational citizenship behavior among university academicians in Northern Nigeria. The goal of the pilot study was to assess the viability, length of time, cost, and negative consequences of self-efficacy on the long-term survival of OCB among universities in Nigeria with the aim of improving the questionnaire's design before it’s full implementation. Three experts from Management, Accounting, and Strategic Management carried out an evaluation of the research instrument, with the goal of ensuring that the questionnaires were consistent so that responders would not have problems while filling them out. The exploratory factor analysis (EFA); which checks for reliability, and the Cronbach alpha values, were used to analyze the content and face validity of the instrument, using the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS) Version 26. The model's components and elements used in this study were all derived from earlier research. A sample size of 36 respondents was used in this study. These respondents were drawn from several Universities from across northern Nigeria. According to the data, all of the constructs in the model had a Cronbach alpha value of greater than 0.7. Consequently, all of the instrument's components were kept. This research is vital in contributing to literature on methodological multivariate studies, quantitative OCB research, and university’s long-term growth and survival.
References
Connelly, L. M. (2008). Pilot studies. Medsurg nursing, 17(6), 411. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2008.17.7.29056
Cooper, D., & Schindler, P. S. (2011). Business Research Methods'. McGraw-Hill. Americas, New York.
Gorsuch, R. L. (1988). Exploratory factor analysis Handbook of multivariate experimental psychology (pp. 231-258): Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0893-5_6
Hadi, N. U., Abdullah, N., & Sentosa, I. (2016). An easy approach to exploratory factor analysis: Marketing perspective. Journal of Educational and Social Research, 6(1), 215 .doi: 10.5901/jesr.2016.v6n1p215
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Canonical correlation: A supplement to multivariate data analysis. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective, 7th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall Publishing: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
Hill, R. (1998). What sample size is “enough” in internet survey research. Interpersonal Computing and Technology: An electronic journal for the 21st century, 6(3-4), 1-12.
Isaac, S., & Michael, W. B. (1995). Handbook in research and evaluation: A collection of principles, methods, and strategies useful in the planning, design, and evaluation of studies in education and the behavioral sciences: Edits publishers.
Jung, S., & Lee, S. (2011). Exploratory factor analysis for small samples. Behavior research methods, 43(3), 701-709. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-011-0077-9
Kline, P. (2014). An easy guide to factor analysis: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315788135
Pearson, R. H. (2008). Recommended sample size for conducting exploratory factor analysis on dichotomous data: University of Northern Colorado.
Ramayah, T., Cheah, J., Chuah, F., Ting, H., & Memon, M. A. (2018). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using smartPLS 3.0. An updated guide and practical guide to statistical analysis.
Sang, L. T., Mail, R., Abd Karim, M. R., Ulum, Z. K. A. B., Mufli, M., & Lajuni, N. (2017). Pretesting and Piloting the Research Instrument to Examine the Central Roles of Risk Perception and Attitude towards Financial Investment Behavioural Intention among Malaysians. Journal of the Asian Academy of Applied Business (JAAAB), 97-97.
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2012). Research methods for business students (6. utg.). Harlow: Pearson.
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach: john wiley & sons.
Zainudin, A., Habsah, M., Fauzilah, S., Abu Shams Mohammad, M. H., & Kamaruzaman, J. (2017). Social business efficiency: Instruments development and validation procedure using structural equation modelling. International Business Management, 11(1), 222-231.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).