Analysis of the Impact of Science, Technology and Innovation on Economic Growth in the Pearl River West Economic Belt
Abstract
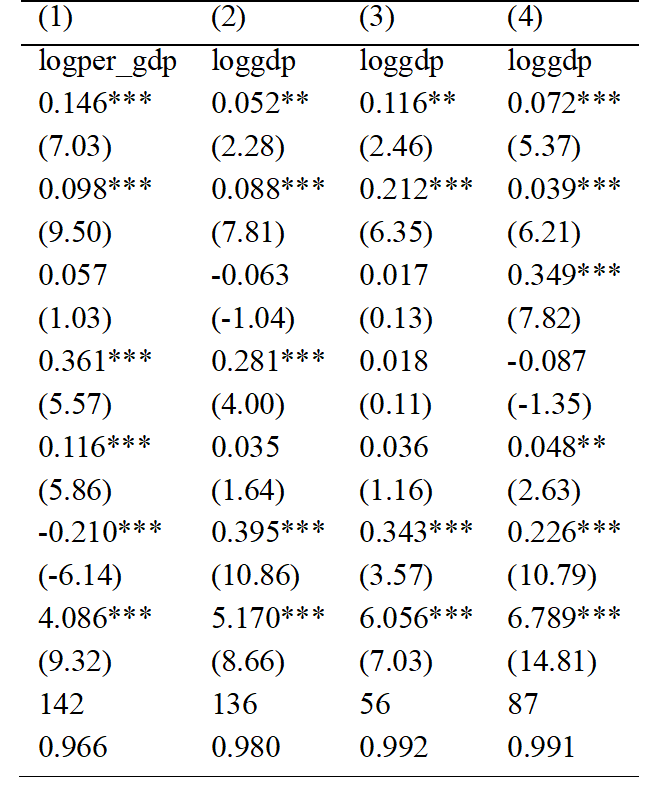
Science and technology innovation has an important impact on economic growth. This paper summarises the relevant theories of domestic and foreign authors on the analysis of the impact of science and technology innovation on economic growth, and combines them with the reality of science and technology innovation on economic growth in the Pearl River West Economic Belt, and argues that there is a certain amount of science and technology innovation outputs in the Pearl River West Economic Belt, which, in turn, promotes economic growth. This paper empirically analyses the impact of STI on the economic growth of the Pearl River-West River Economic Belt by using the statistical data from 2000 to 2020 of the 11 major cities involved in the belt (i.e., Guangzhou, Foshan, Zhaoqing, Yunfu, Nanning, Liuzhou, Wuzhou, Guigang, Baise, Laibin and Chongzuo). The results show that the impact of S&T innovation on the economic growth of the Pearl River-West River Economic Belt is positively correlated, indicating that S&T innovation can promote the economic growth of the Pearl River-West River Economic Belt. And this effect is robust.
References
Ji, Y., Wu, Y., & Bai, Y. (2008). Science and technology innovation multiplier effect in China's economic growth: Micro-mechanism and macro-measurement. The Economist, 1, 55–62.
Lin, L., & Chen, H. (2021). Impact of technological innovation on regional economic growth in Zhejiang Province. Quality and Market.
Ning, H., & Tang, J. (2021). Science and technology innovation and economic growth: A VAR model study based on Tianjin data. Qinghai Science and Technology, 28(03), 10–15.
Yang, K., & Min, C. (2019). Research on the driving role of technological innovation on the quality of economic growth: Taking Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao Greater Bay Area as an example. Contemporary Economic Management, 41(12), 29–37.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
























